Service Orchestration¶
What you'll build¶
When information from several services are required to construct a response to a client request, service chaining needs to be implemented. That is, several services are integrated based on some business logic and exposed as a single, aggregated service.
In this tutorial, when a client sends a request for a medical appointment, the Micro Integrator performs several service call to multiple back-end services in order to construct the response that includes all the necessary details.
To build this mediation flow, you will update the API resource from the Message Transformation tutorial to send messages through the Micro Integrator to the back-end service using the Call mediator instead of the Send mediator. The Call mediator allows you to specify all service invocations one after the other within a single sequence. You will then use the PayloadFactory mediator to take the response from one back-end service and change it to the format that is accepted by the other back-end service.
Let's get started!¶
Step 1: Set up the workspace¶
Set up WSO2 Integration Studio as follows:
- Download the relevant WSO2 Integration Studio based on your operating system.
-
Set up the project from the Message Transformation tutorial:
Note
This tutorial is a continuation of the Message Transformation tutorial.
- Download the pre-packaged project.
- Open WSO2 Integration Studio and go to File -> Import.
- Select Existing WSO2 Projects into workspace under the WSO2 category, click Next, and then upload the prepackaged project.
Step 2: Develop the integration artifacts¶
Create new Endpoints¶
Let's create new HTTP endpoints to represent the back-end services that are required for checking the channelling fee and to settle the payment.
- Right click SampleServicesConfigs in the Project Explorer and navigate to New -> Endpoint.
- Ensure Create a New Endpoint is selected and click Next.
-
Enter the details given below:
Property Value Description Endpoint Name ChannelingFeeEP The name of the endpoint. Endpoint Type HTTP EndpointIndicates that the back-end service is HTTP. URI Template http://localhost:9090/{uri.var.hospital}/categories/appointments/{uri.var.appointment_id}/feeThe template for the request URL expected by the back-end service. Method GETThis endpoint artifact will be used to get information from the back-end service. Static Endpoint
Select this option because we are going to use this endpoint only in this ESB Config module and will not reuse it in other projects. Note: If you need to create a reusable endpoint, save it as a Dynamic Endpoint in either the Configuration or Governance Registry. Save Endpoint in SampleServicesConfigsThis is the ESB Config module. -
Click Finish.
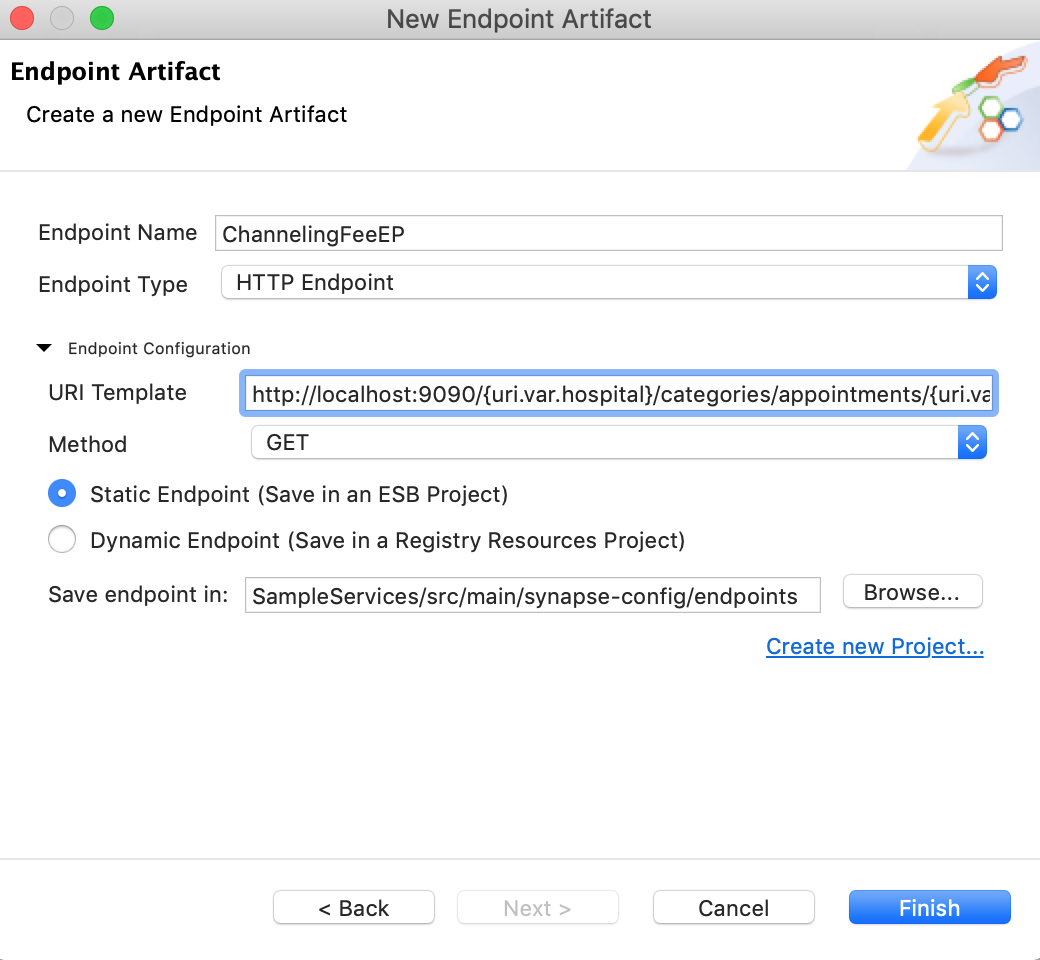
-
Create another endpoint for the Settle Payment back-end service and specify the details given below:
Property Value Description Endpoint Name SettlePaymentEP The name of the endpoint. Endpoint Type HTTP EndpointIndicates that the back-end service is HTTP. URI Template http://localhost:9090/healthcare/paymentsThe template for the request URL expected by the back-end service. Method POSTThis endpoint artifact will be used to post informtion to the back-end service. Static Endpoint
Select this option because we are going to use this endpoint only in this ESB Config module and will not reuse it in other projects. Note: If you need to create a reusable endpoint, save it as a Dynamic Endpoint in either the Configuration or Governance Registry. Save Endpoint in SampleServicesConfigsThis is the ESB Config module. -
Click Finish.
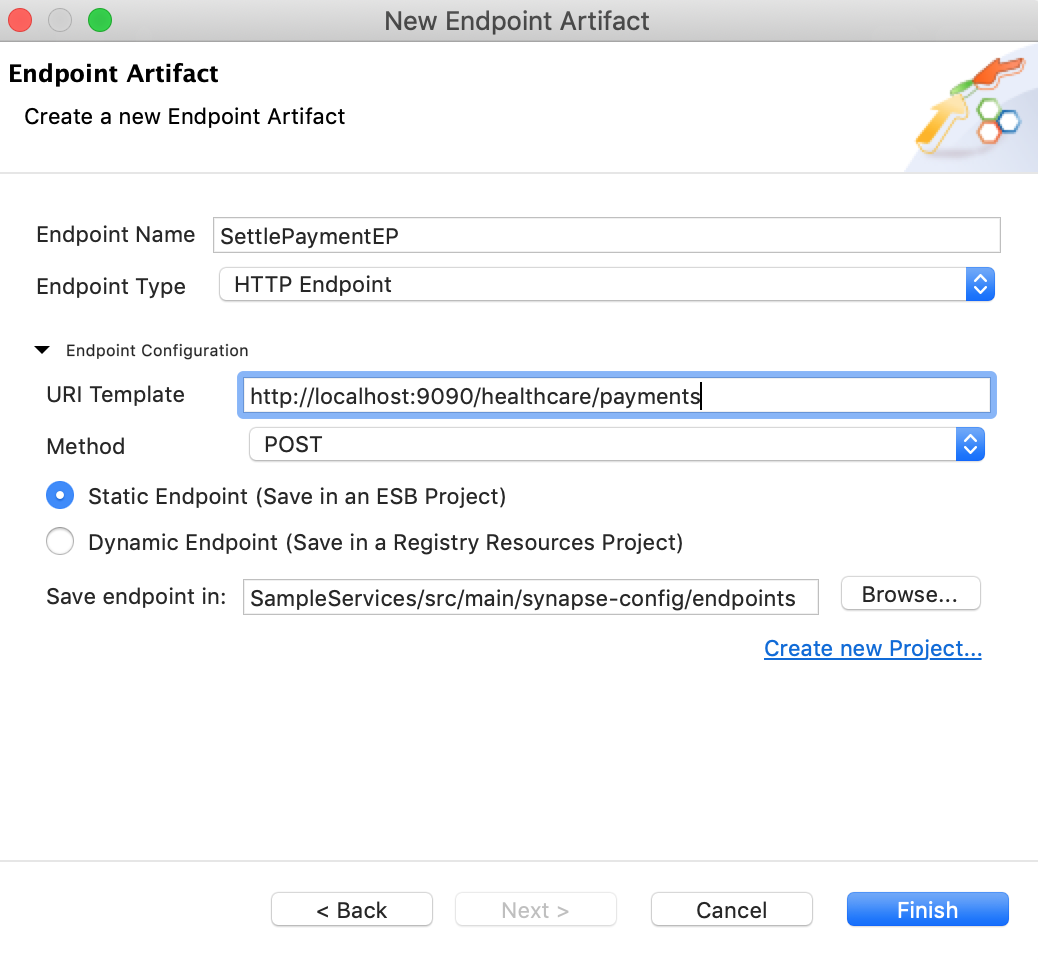
You have now created the additional endpoints that are required for this tutorial.
Update the mediation flow¶
You can now start updating the API resource with the mediation flow.
-
Add a new Property mediator just after the Get Hospital Property mediator in the In Sequence of the API resource to retrieve and store the card number that is sent in the request payload.
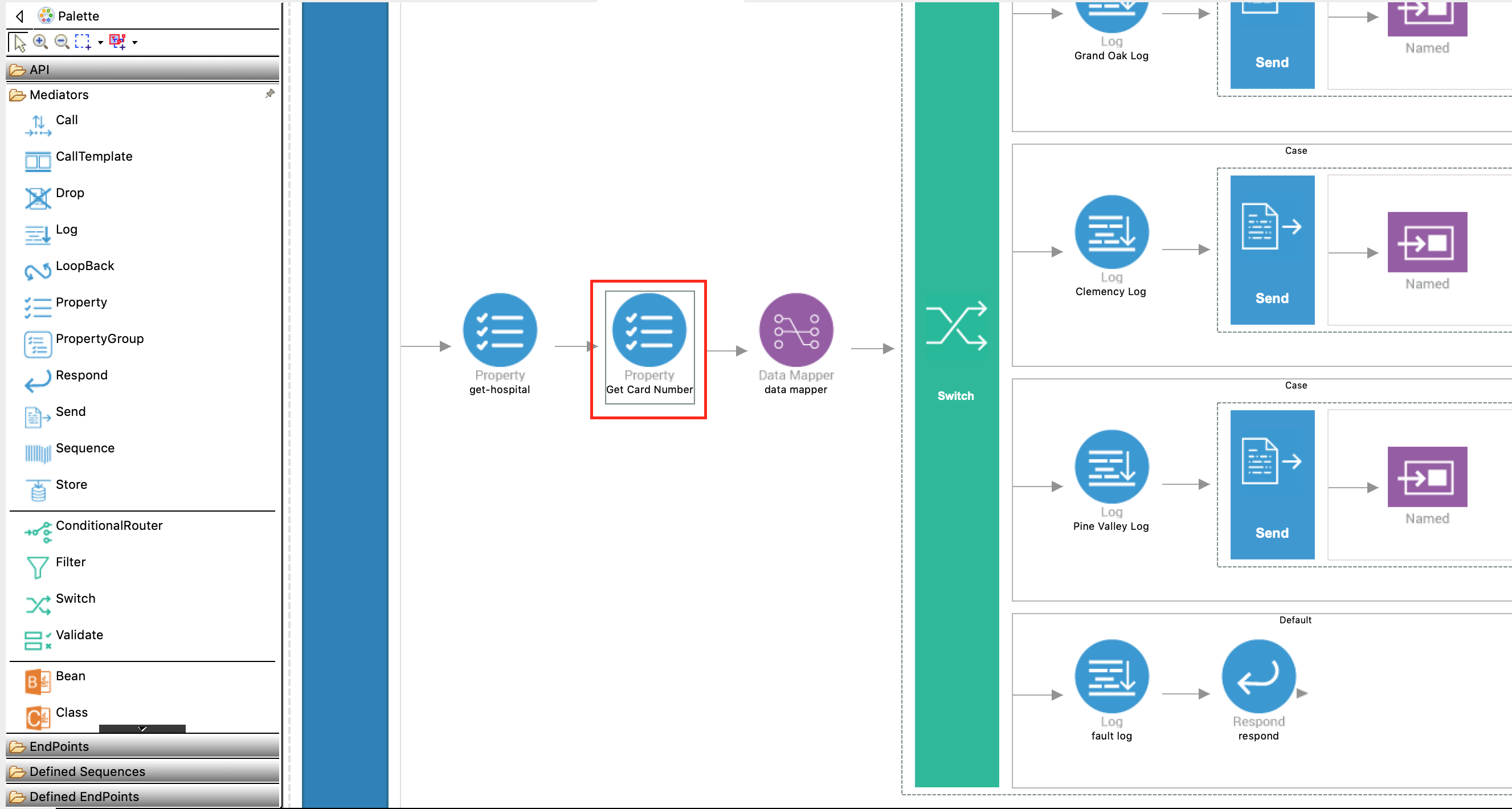
-
With the Property mediator selected, access the Properties tab and specify the following details:
Property Description Property Name Enter New Property....New Property Name Enter card_number.Property Action Enter set.Value Follow the steps given below to specify the expression:

- Click the Ex button before the Value field. This specifies the value type as expression.
- Now, click the f button to open the Expression Selector dialog box.
- Enter
json-eval($.cardNo)as the expression value.
Description Get Card Number -
Go to the first case box of the Switch mediator. Add a Property mediator just after the Log mediator to store the value for the
uri.var.hospitalvariable that will be used when sending requests to ChannelingFeeEP service.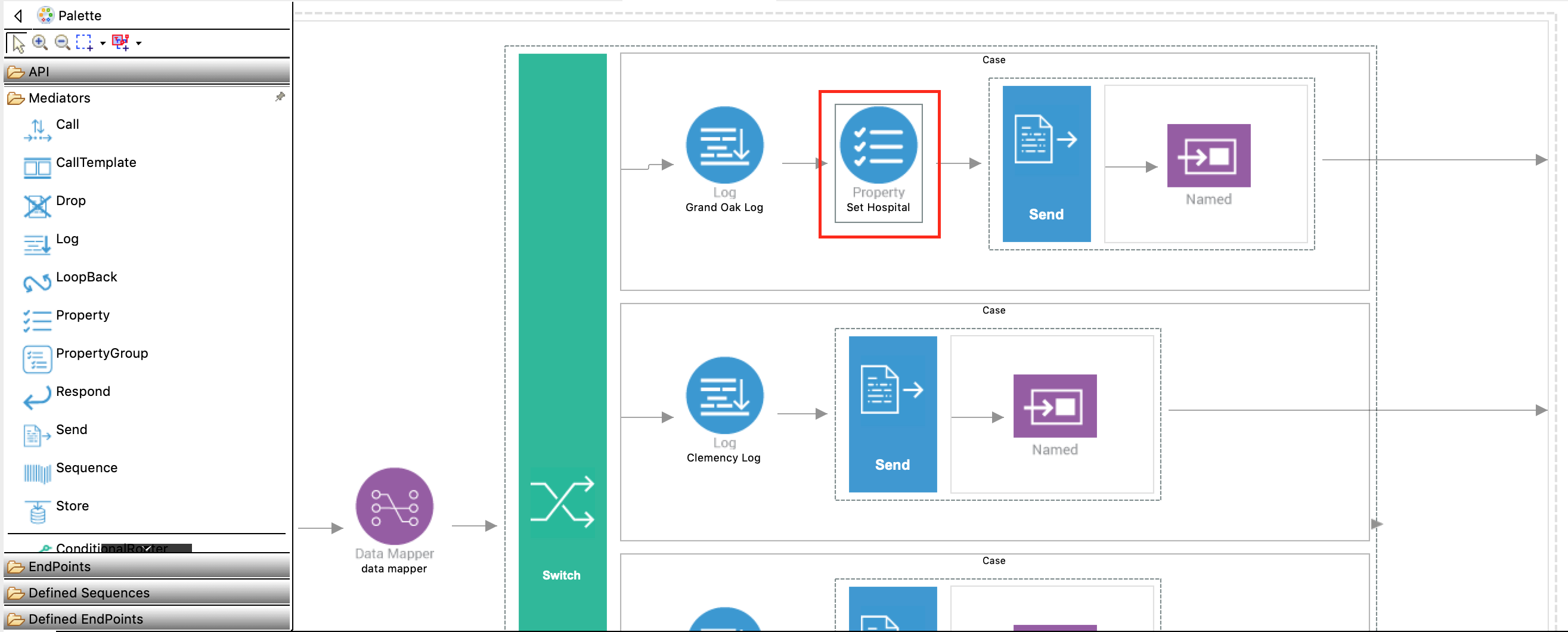
-
With the Property mediator selected, access the Properties tab and specify the following details:
Property Description Property Name Enter New Property....New Property Name Enter uri.var.hospital.Property Action Enter set.Property Data Type STRING Value grandoaksDescription Set Hospital Variable -
Similarly, add property mediators in the other two case boxes in the Switch mediator. Change only the Value field as follows:
- Case 2:
clemency - Case 3:
pinevalley
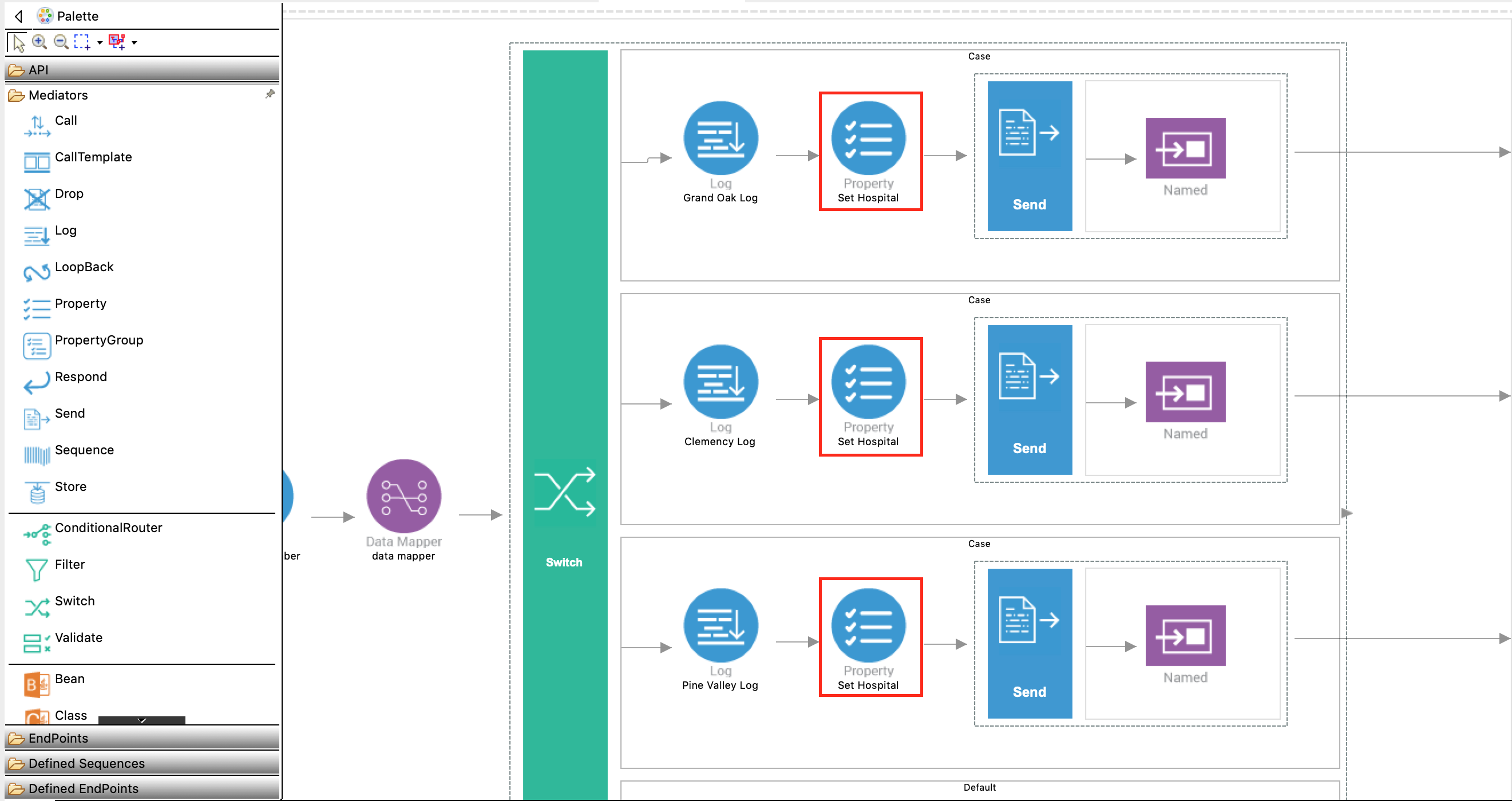
- Case 2:
-
Delete the Send mediator by right clicking on the mediator and selecting Delete from Model. Replace this with a Call mediator from the Mediators palette and add GrandOakEP from the Defined Endpoints palette to the empty box adjoining the Call mediator.
-
Replace the Send mediators in the following two case boxes as well and add ClemencyEP and PineValleyEP to the respective boxes adjoining the Call mediators.
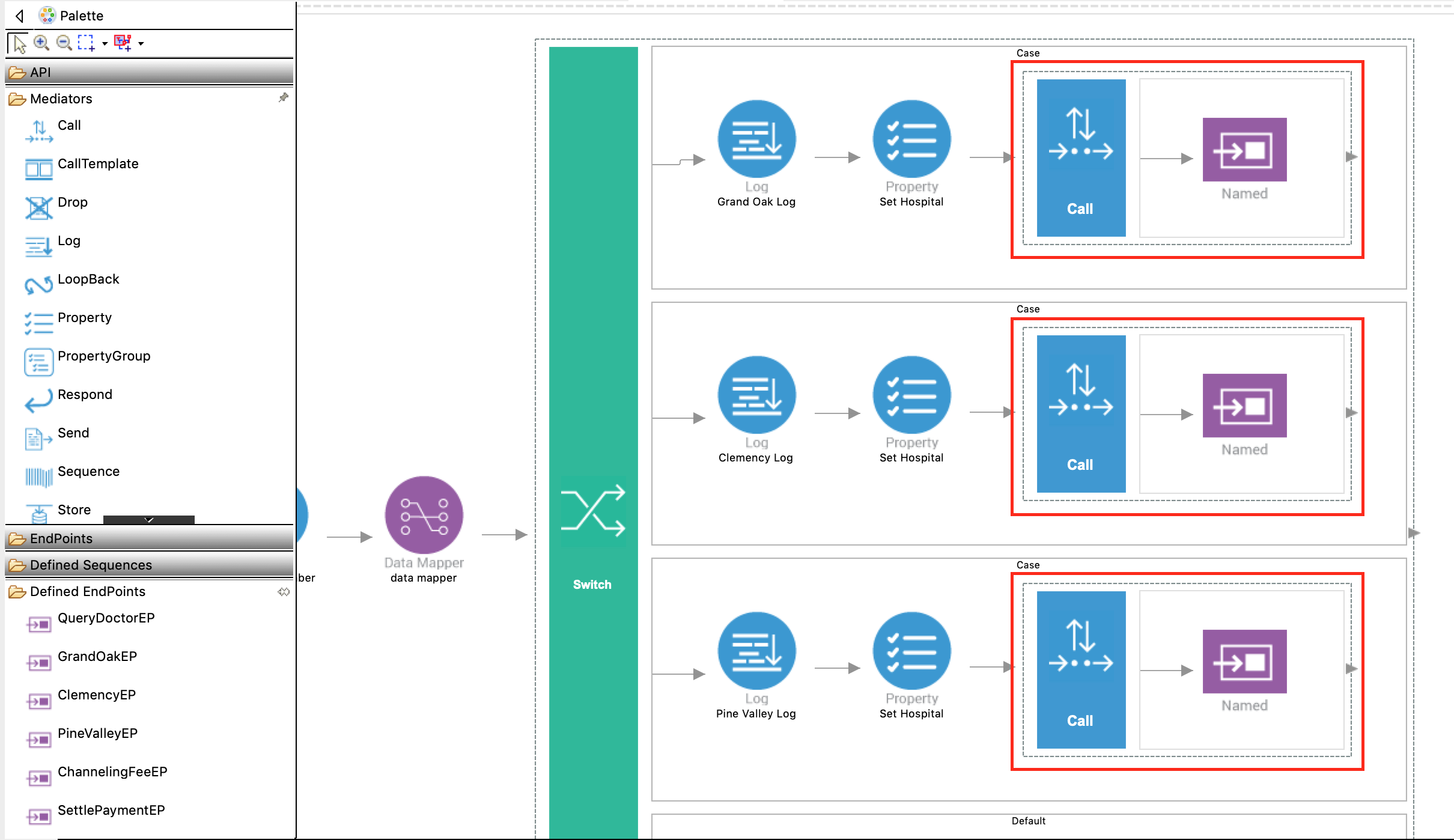
Info
Using the Call mediator allows us to define other service invocations following this mediator.
Let's use Property mediators to retrieve and store the values that you get from the response you receive from GrandOakEP, ClemencyEP, or PineValleyEP.
-
Next to the Switch mediator, add a Property mediator to retrieve and store the value sent as
appointmentNumber.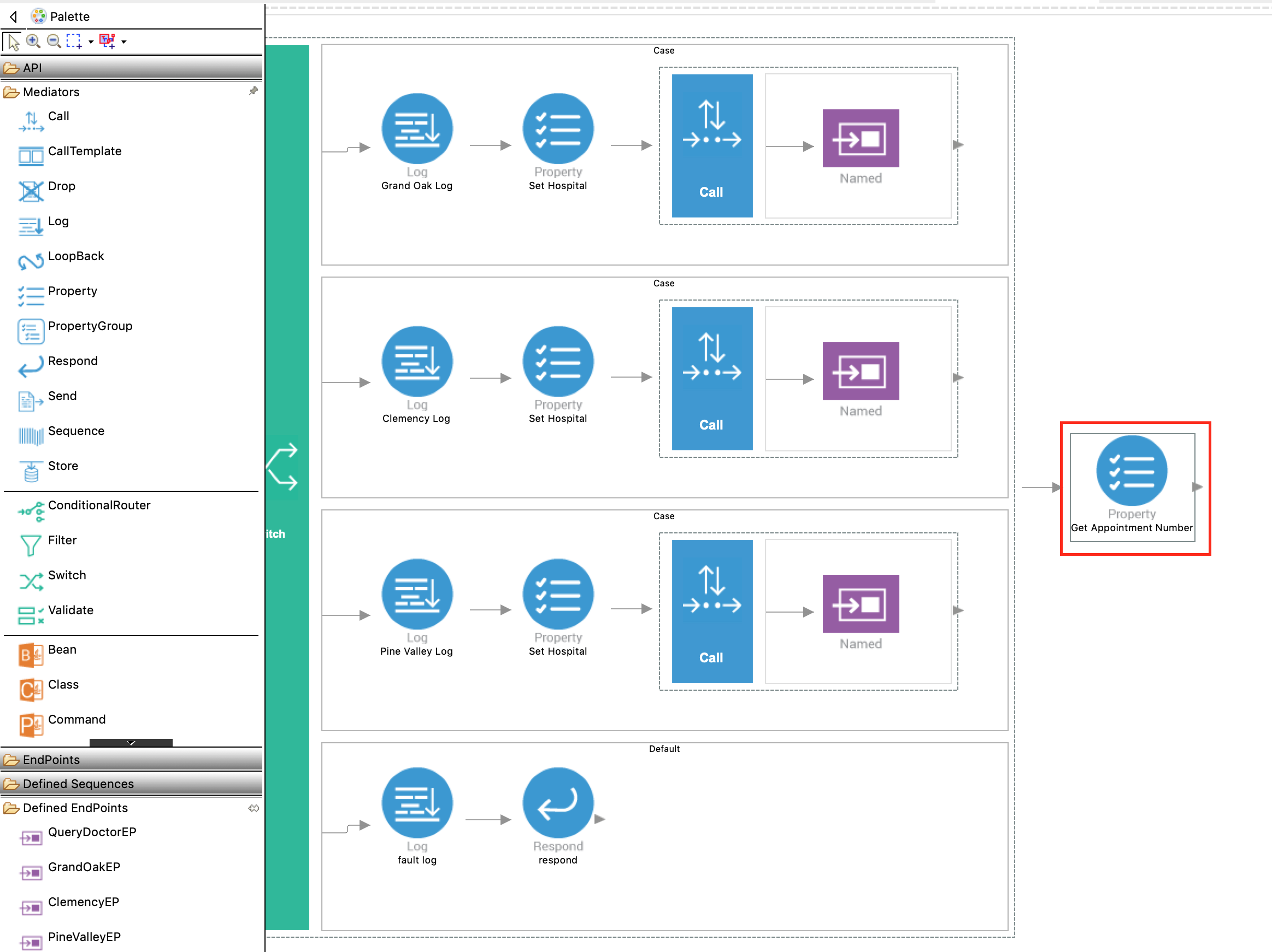
-
With the Property mediator selected, access the Properties tab and specify the following details:
Property Description Property Name Select New Property. New Property Name Enter uri.var.appointment_id.
This value is used when invoking ChannelingFeeEP.Property Action Select set
Value Follow the steps given below to specify the expression:

- Click the Ex button before the Value field. This specifies the value type as expression.
- Now, click the f button to open the Expression Selector dialog box.
- Enter
json-eval($.appointmentNumber)as the expression value.
Description Get Appointment Number Note
You derive the Value Expression in the above table from the following response that is received from GrandOakEP, ClemencyEP, or PineValleyEP:
{"appointmentNumber":1, "doctor": {"name":"thomas collins", "hospital":"grand oak community hospital", "category":"surgery","availability":"9.00 a.m - 11.00 a.m", "fee":7000.0}, "patient": {"name":"John Doe", "dob":"1990-03-19", "ssn":"234-23-525", "address":"California", "phone":"8770586755", "email":"[email protected]"}, "fee":7000.0, "confirmed":false} -
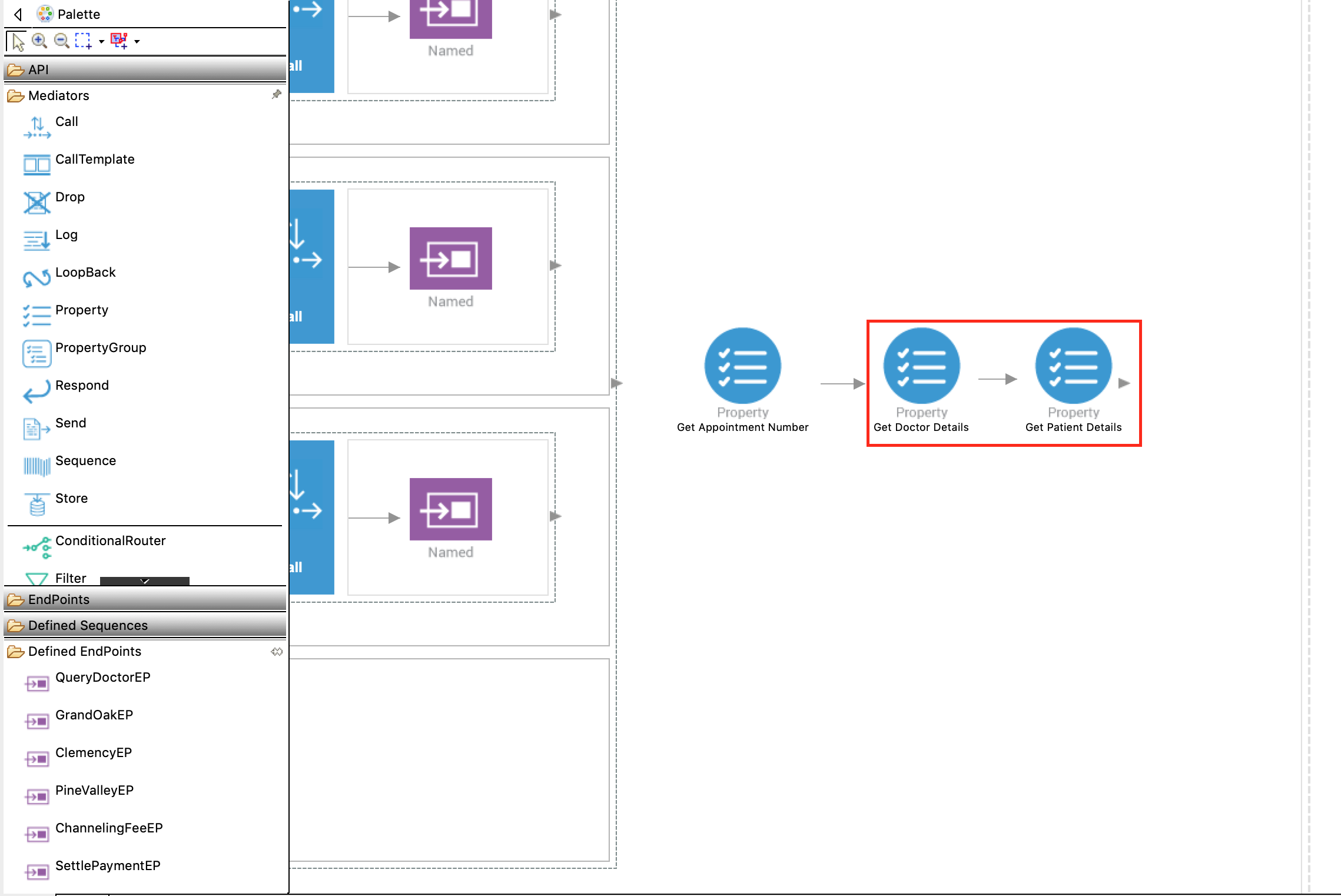
Similarly, add two more Property mediators. They will retrieve and store the
doctordetails andpatientdetails respectively from the response that is received from GrandOakEP, ClemencyEP, or PineValleyEP.-
To store
doctordetails:Property Description Property Name Select New Property. New Property Name Enter doctor_details.Property Action Select set. Value Follow the steps given below to specify the expression:

- Click the Ex button before the Value field. This specifies the value type as expression.
- Now, click the f button to open the Expression Selector dialog box.
- Enter
json-eval($.doctor)as the expression value.
Description Get Doctor Details -
To store
patientdetails:Property Description Property Name Select New Property New Property Name Enter patient_detailsProperty Action Select set Value Follow the steps given below to specify the expression:

- Click the Ex button before the Value field. This specifies the value type as expression.
- Now, click the f button to open the Expression Selector dialog box.
- Enter
json-eval($.patient)as the expression value.
Description Get Patient Details
-
-
Add a Call mediator and add the ChannelingFeeEP endpoint from the Defined Endpoints palette to the empty box adjoining the Call mediator.
- Add a Property mediator adjoining the Call mediator box to retrieve and store the value sent as
actualFee. -
Access the Property tab of the mediator and specify the following details:
Property Description Property Name Select New Property New Property Name Enter actual_feeNote: This value is used when invoking SettlePaymentEP.Property Action Select set Value Follow the steps given below to specify the expression:

- Click the Ex button before the Value field. This specifies the value type as expression.
- Now, click the f button to open the Expression Selector dialog box.
- Enter
json-eval($.actualFee)as the expression value.
Description Get Actual Fee 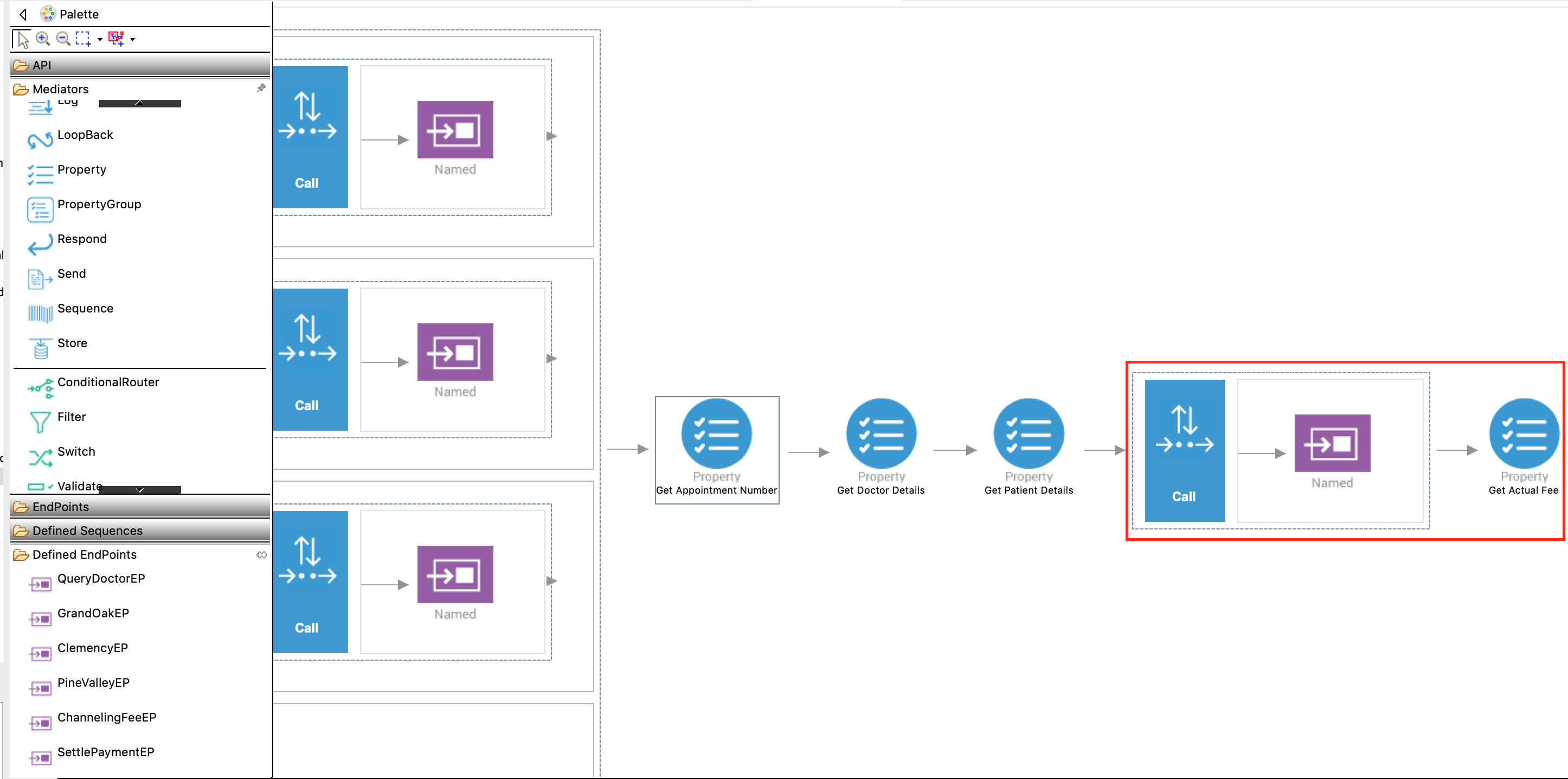
Note
You derive the Value Expression in the above table from the following response that is received from ChannelingFeeEP:
{"patientName":" John Doe ", "doctorName":"thomas collins", "actualFee":"7000.0"} -
Let's use the PayloadFactory mediator to construct the following message payload for the request sent to SettlePaymentEP.
{"appointmentNumber":2, "doctor":{ "name":"thomas collins", "hospital":"grand oak community hospital", "category":"surgery", "availability":"9.00 a.m - 11.00 a.m", "Fee":7000.0 }, "patient":{ "name":"John Doe", "Dob":"1990-03-19", "ssn":"234-23-525", "address":"California", "phone":"8770586755", "email":"[email protected]" }, "fee":7000.0, "Confirmed":false, "card_number":"1234567890" } -
Add a PayloadFactory mediator (from the mediators palette) next to the Property mediator to construct the above message payload.
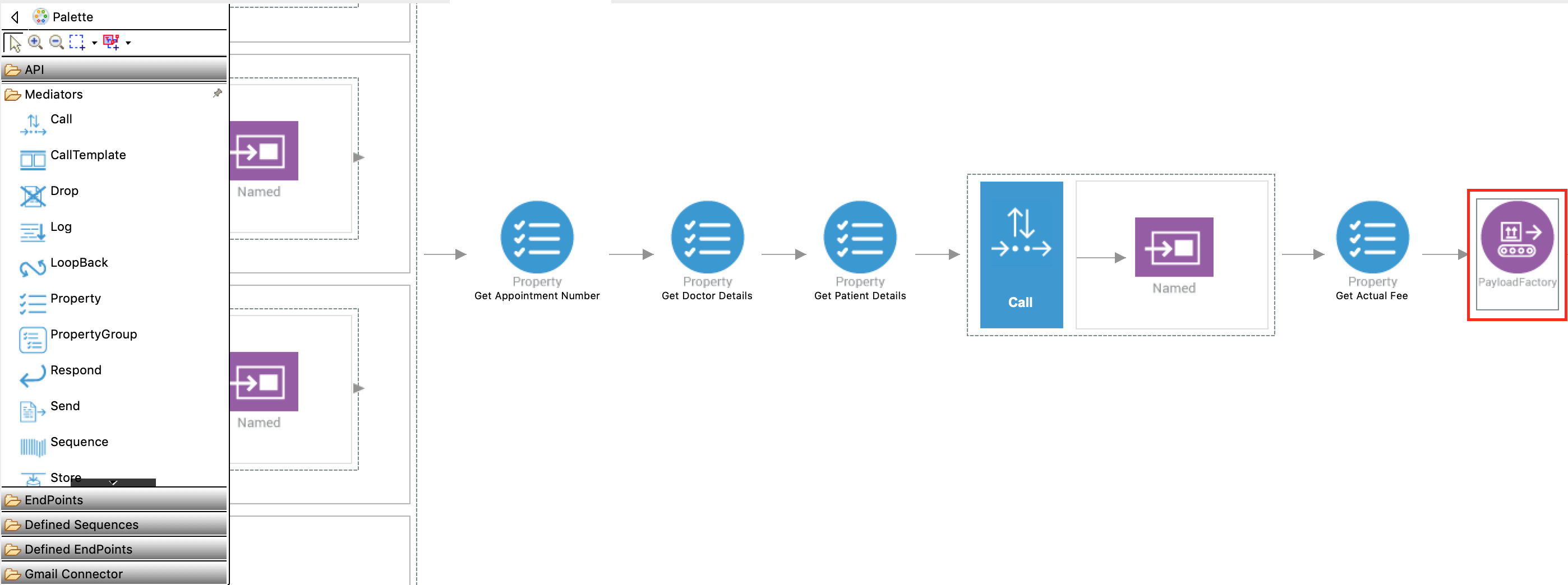
-
With the Payloadfactory mediator selected, access the properties tab of the mediator and specify the following details:
Property Descripttion Payload Format Select Inline Media Type Select json Payload {"appointmentNumber":$1, "doctor":$2, "patient":$3, "fee":$4, "confirmed":"false", "card_number":"$5"}This is the message payload to send with the request to SettlePaymentEP. In this payload, $1, $2, $3, $4, and $5 indicate variables. -
To add the arguments for the PayloadFactory mediator:
- Click the plus icon (
 ) in the Args field to open the PayloadFactoryArgument dialog.
) in the Args field to open the PayloadFactoryArgument dialog. -
Enter the following information in the PayloadFactoryArgument dialog box. This provides the argument that defines the actual value of the first variable (used in the format definition given in the previous step).
Tip
To avoid getting an error message, first select the Media Type before providing the Payload.
Property Description Argument Type Select Expression.Argument Expression Follow the steps given below to specify the expression:
- Click the text box for the Argument Expression field. This opens the Expression Selector dialog.
- Select Expression from the list.
-
Enter
$ctx:uri.var.appointment_id. Note that the$ctxmethod is similar to using theget-propertymethod. This method checks in the message context. - Click OK.
Evaluator Select xml. This indicates that the expression is provided in XML.
- Click the plus icon (
-
Similarly, click Add and add more arguments to define the other variables that are used in the message payload format definition. Use the following as the Value for each of them:
$ctx:doctor_details$ctx:patient_details$ctx:actual_fee$ctx:card_number
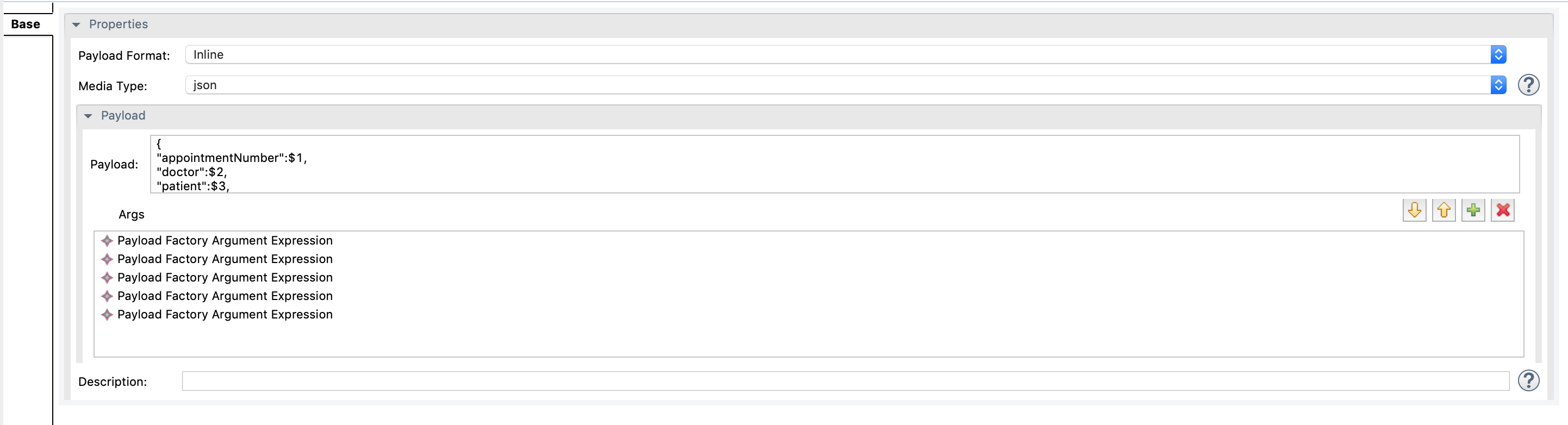
-
Add a Call mediator and add SettlePaymentEP from the Defined Endpoints palette to the empty box adjoining the Call mediator.
- Add a Respond mediator to send the response to the client.
You should now have a completed configuration that looks like this:
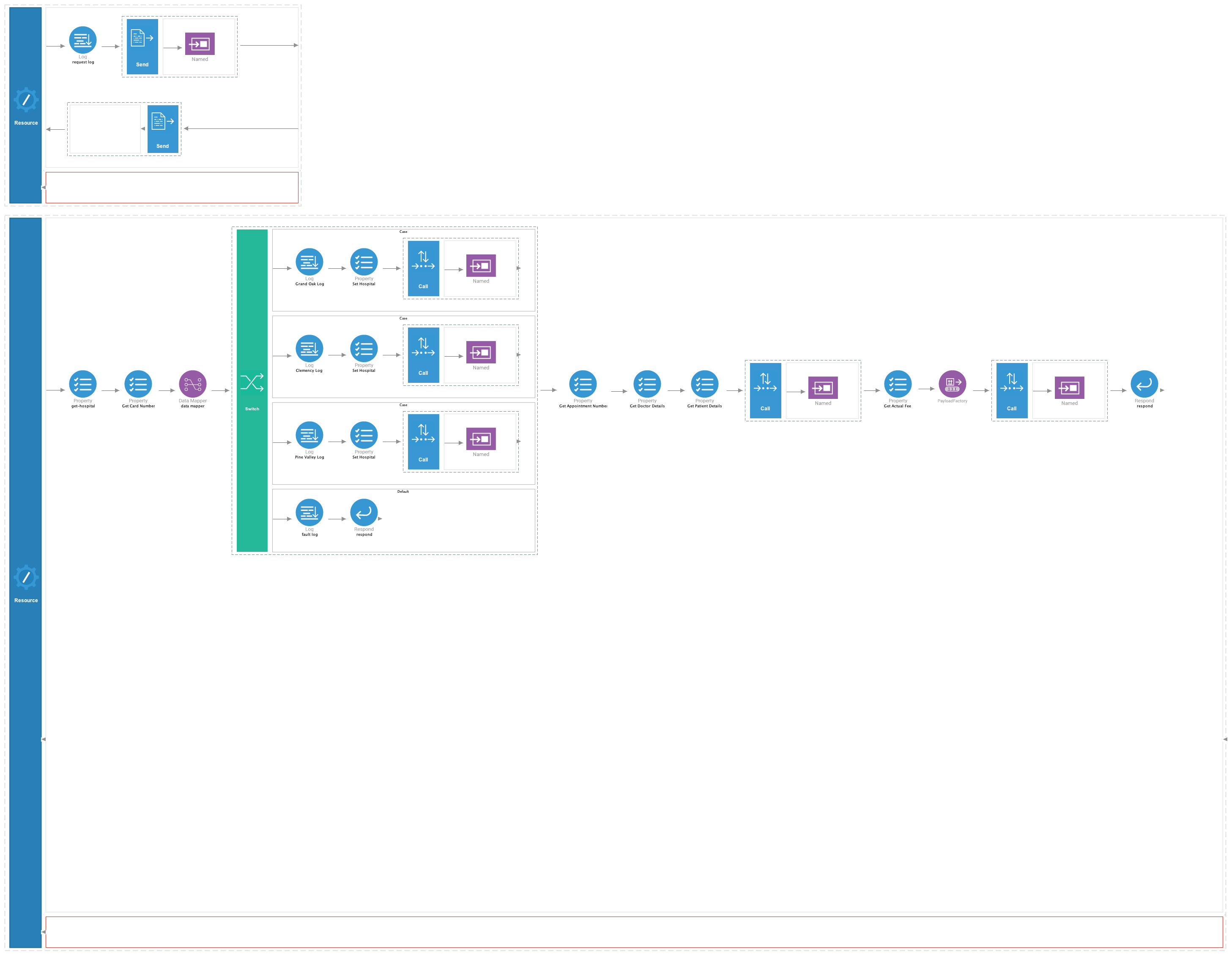
Step 3: Package the artifacts¶
Package the artifacts in your composite exporter (SampleServicesCompositeExporter) to be able to deploy the artifacts in the server.
- Open the
pom.xmlfile in the composite exporter. -
Ensure that the following projects and artifacts are selected in the POM file.
- SampleServicesCompositeExporter
HealthcareAPIClemencyEPGrandOakEPPineValleyEPChannelingFeeEPSettlePaymentEP
- SampleServicesRegistryResources
- SampleServicesCompositeExporter
-
Save the changes.
Step 4: Build and run the artifacts¶
To test the artifacts, deploy the packaged artifacts in the embedded Micro Integrator:
- Right-click the composite exporter module and click Export Project Artifacts and Run.
- In the dialog box that opens, confirm that the required artifacts from the composite exporter module are selected.
- Click Finish.
The artifacts will be deployed in the embedded Micro Integrator and the server will start.
- See the startup log in the Console tab.
- See the URLs of the deployed services and APIs in the Runtime Services tab.
Step 5: Test the use case¶
Let's test the use case by sending a simple client request that invokes the service.
Start the back-end service¶
- Download the JAR file of the back-end service from here.
- Open a terminal, navigate to the location where your saved the back-end service.
-
Execute the following command to start the service:
java -jar Hospital-Service-JDK11-2.0.0.jar
Send the client request¶
Let's send a request to the API resource to make a reservation. You can use the embedded HTTP Client of WSO2 Integration Studio as follows:
-
Open the HTTP Client of WSO2 Integration Studio.
Tip
If you don't see the HTTP Client pane, go to Window -> Show View - Other and select HTTP Client to enable the client pane.
-
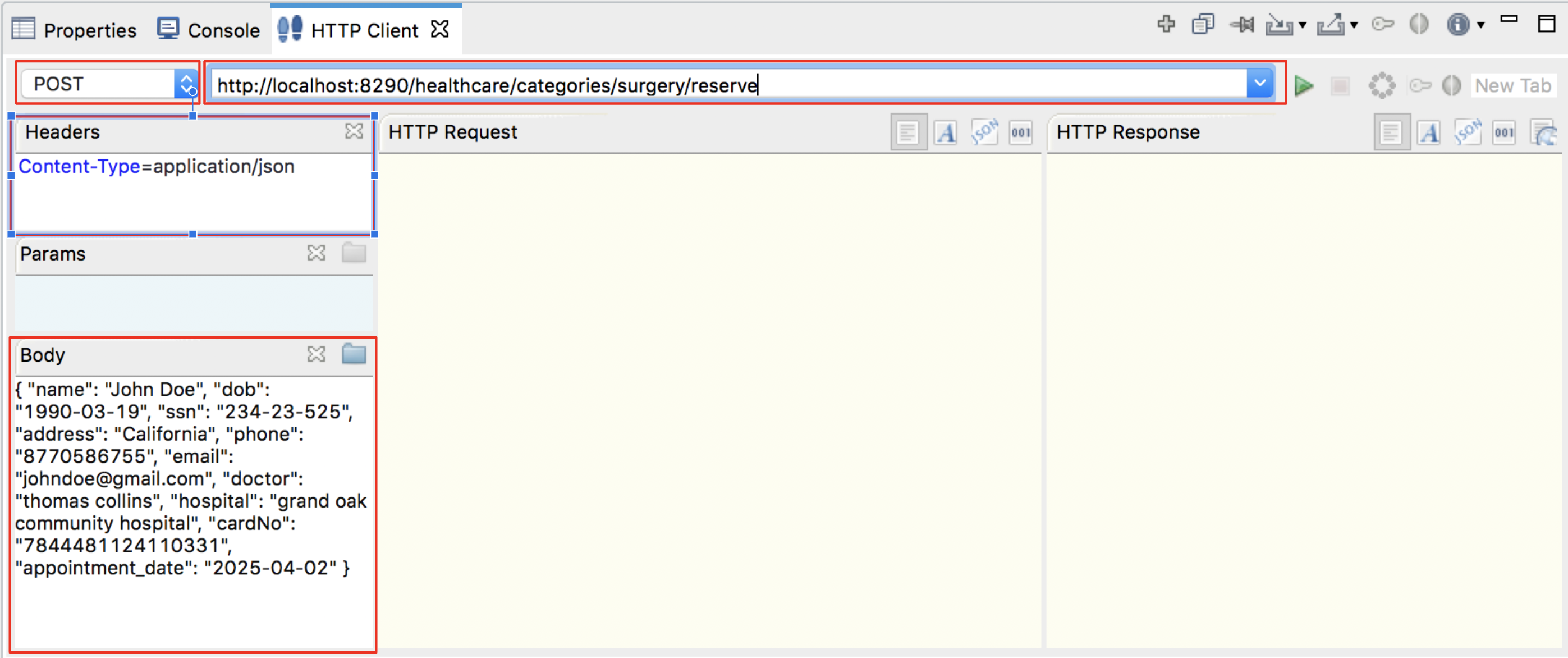
Enter the request information as given below and click the Send icon (
 ).
).Method POSTHeaders Content-Type=application/jsonURL http://localhost:8290/healthcare/categories/surgery/reserve-
The URI-Template format that is used in this URL was defined when creating the API resource:
http://.: /categories/{category}/reserve
Body { "name": "John Doe", "dob": "1940-03-19", "ssn": "234-23-525", "address": "California", "phone": "8770586755", "email": "[email protected]", "doctor": "thomas collins", "hospital": "grand oak community hospital", "cardNo": "7844481124110331", "appointment_date": "2025-04-02" }- This JSON payload contains details of the appointment reservation, which includes patient details, doctor, hospital, and data of appointment.
-
The URI-Template format that is used in this URL was defined when creating the API resource:
If you want to send the client request from your terminal:
- Install and set up cURL as your REST client.
- Create a JSON file named
request.jsonwith the following request payload.{ "name": "John Doe", "dob": "1940-03-19", "ssn": "234-23-525", "address": "California", "phone": "8770586755", "email": "[email protected]", "doctor": "thomas collins", "hospital": "grand oak community hospital", "cardNo": "7844481124110331", "appointment_date": "2025-04-02" } - Open a terminal and navigate to the directory where you have saved the
request.jsonfile. - Execute the following command.
curl -v -X POST --data @request.json http://localhost:8290/healthcare/categories/surgery/reserve --header "Content-Type:application/json"
Analyze the response¶
You will see the response received to your HTTP Client:
{
"appointmentNo":1,
"doctorName":"thomas collins",
"patient":"John Doe",
"actualFee":7000.0,
"discount":20,
"discounted":5600.0,
"paymentID":"480fead2-e592-4791-941a-690ad1363802",
"status":"Settled"
}You have now explored how the Micro Integrator can do service chaining using the Call mediator and transform message payloads from one format to another using the PayloadFactory mediator.
Top