Cache Mediator¶
When a message enters a message flow, the Cache mediator checks whether the incoming message is similar to a previous message that was received
within a specified period of time. This is done by evaluating the hash value of incoming messages. If a similar message was identified before, the Cache mediator executes the onCacheHit sequence (if specified), fetches the cached response, and prepares the Micro Integrator to send the response. The onCacheHit sequence can send back the response message using the Respond Mediator. If the onCacheHit sequence is not specified, the cached response is sent back to the requester and the message is not passed on. If a similar message has not been seen before, then the message is passed on.
Info
- The Cache mediator is a content-aware mediator.
- The Cache mediator supports only local caching. It does not support distributed caching.
Syntax¶
<cache [timeout="seconds"] [collector=(true | false)] [maxMessageSize="in-bytes"] >
<onCacheHit [sequence="key"]>
(mediator)+
</onCacheHit>?
<protocol type="http" >?
<methods>comma separated list</methods>
<headersToExcludeInHash>comma separated list</headersToExcludeInHash>
<responseCodes>regular expression</responseCodes>
<enableCacheControl>(true | false)</enableCacheControl>
<includeAgeHeader>(true | false)</includeAgeHeader>
<hashGenerator>class</hashGenerator>
</protocol>
<implementation [maxSize="int"]/>
</cache>Info
In a message flow, you can use the cache mediator as a finder (in the incoming path to check the request) or as a collector (in the outgoing path to cache the response). It is not possible to have more than one cache mediator in the same message flow because mediation is terminated after the finder on a cache hit, and the response is not passed on to the next finder after a cache hit. See the Example 1 given below.
Note
The message needs to be explicitly marked as RESPONSE using the following property when collecting the cached response in the same sequence after using the call mediator. This will not be required if the back end is called via send mediator. See the Example 1 given below.
<property name="RESPONSE" value="true" scope="default" type="STRING"/>Configuration¶
Cache Mediator as a Finder¶
The parameters available to configure the Cache mediator as a Finder are as follows.
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Cache Type | This parameter specifies whether the Cache mediator should be in the incoming path (to check the request) or in the outgoing path (to cache the response). Possible values are as follows.
|
| Cache Timeout (Seconds) | The time duration that the cache should be retained specified in seconds. The cache expires once this time duration elapses. The default value is 5000 seconds. |
| Maximum Message Size | The maximum size of the message to be cached. This should be specified in bytes. |
| Protocol Type | The protocol type to be cached in the message flow. In the current implementation, HTTP is the only value that you can select. Although the only configuration supported for other protocols is the HashGenerator , you can specify the protocol type to be anything and specify a HashGenerator that you prefer. |
| HTTP Methods | A comma separated list of HTTP methods that should be cached for the HTTP protocol. The default value is *, and it caches all HTTP methods. |
| Headers to Exclude in Hash | A comma separated list of headers to ignore when hashing an incoming messages. If you want to exclude all headers when hashing an incoming message, specify *. |
| Response Codes | Specify the response codes to be cached as a regular expression. If the http status code of a response matches the regular expression, the response should be cached. The default setting is to cache any response code. |
| Hash Generator | This parameter is used to define the logic used by the Cache mediator to evaluate the hash values of incoming messages. The value specified here should be a class that implements the The hash generator is specific to the HTTP protocol. If you are using any other protocol, you need to write a custom hash generator or use one of the following deprecated hash generator classes:
|
| Enable Cache Control Headers | Whether the Cache mediator should honor the Cache-Control header(no-cache, no-store, max-age headers). If you set this to the default value (i.e., |
| Include Age Header | Whether an Age header needs to be included when returning the cached response. |
| Maximum Size | The maximum number of elements to be cached. The default size is 1000. |
| Anonymous | If this option is selected, an anonymous sequence is executed when an incoming message is identified as an equivalent to a previously received message based on the value defined in the Hash Generator field. |
| Sequence Reference | The reference to the onCacheHit sequence to be executed when an incoming message is identified as an equivalent to a previously received message, based on the value defined in the Hash Generator field. The sequence should be created in the registry in order to be specified in this field. You can click either Configuration, Registry, or Governance Registry as applicable to select the required sequence from the resource tree. |
Cache Mediatior as a Collector¶
The parameters available to configure the Cache mediator as a Collector are as follows.
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Cache Type | This parameter specifies whether the mediator should be in the incoming path (to check the request) or in the outgoing path (to cache the response). Possible values are as follows.
|
Examples¶
Following are examples of how you can use the Cache mediator.
Example 1¶
Following is an example where the expected response from the last cache hit is not received because the response is sent once the request comes to the first finder:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<proxy xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" name="cache115" transports="http https" startOnLoad="true">
<description />
<target>
<inSequence>
<cache collector="false" timeout="60">
<protocol type="HTTP">
<methods>POST</methods>
<headersToExcludeInHash />
<responseCodes>.*</responseCodes>
<enableCacheControl>false</enableCacheControl>
<includeAgeHeader>false</includeAgeHeader>
<hashGenerator>org.wso2.carbon.mediator.cache.digest.HttpRequestHashGenerator</hashGenerator>
</protocol>
</cache>
<call>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://demo0585968.mockable.io/some" />
</endpoint>
</call>
<property name="RESPONSE" value="true" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<log level="full" />
<cache collector="true" />
<property name="RESPONSE" value="false" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<cache collector="false" timeout="60">
<protocol type="HTTP">
<methods>POST</methods>
<headersToExcludeInHash />
<responseCodes>.*</responseCodes>
<hashGenerator>org.wso2.carbon.mediator.cache.digest.HttpRequestHashGenerator</hashGenerator>
</protocol>
</cache>
<call>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://demo0585968.mockable.io/hello" />
</endpoint>
</call>
<property name="RESPONSE" value="true" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<log level="full" />
<cache collector="true" />
<respond />
</inSequence>
</target>
</proxy> Example 2¶
According to this example configuration, when the first message is sent
to the endpoint, the cache is not hit. The Cache mediator configured in
the Out sequence caches the response to this message.
When a similar message is sent to the endpoint for the second time, the
previous response is directly fetched from the cache and sent to the
requester. This happens because the onCacheHit
sequence is not defined in this configuration.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<sequence name="main">
<in>
<cache collector="false" maxMessageSize="10000" timeout="20">
<protocol type="HTTP">
<methods>POST</methods>
<headersToExcludeInHash/>
<responseCodes>2[0-9][0-9]</responseCodes>
<enableCacheControl>false</enableCacheControl>
<includeAgeHeader>false</includeAgeHeader>
<hashGenerator>org.wso2.carbon.mediator.cache.digest.HttpRequestHashGenerator</hashGenerator>
</protocol>
<implementation maxSize="100"/>
</cache>
<send>
<endpoint name="inlined">
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
</send>
</in>
<out>
<cache collector="true"/>
<send/>
</out>
</sequence>Example 3¶
According to this example configuration, if you define a cache collector
using the cache mediator in the in sequence, you need to add the
RESPONSE property to consider the message as a
response message.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<api xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" name="cacheAPI" context="/cache">
<resource methods="POST GET" uri-template="/headerapi/*">
<inSequence>
<cache collector="false" timeout="5000">
<protocol type="HTTP">
<methods>GET, POST</methods>
<headersToExcludeInHash>*</headersToExcludeInHash>
<responseCodes>.*</responseCodes>
<enableCacheControl>false</enableCacheControl>
<includeAgeHeader>false</includeAgeHeader>
<hashGenerator>org.wso2.carbon.mediator.cache.digest.HttpRequestHashGenerator</hashGenerator>
</protocol>
</cache>
<call>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
</call>
<property name="RESPONSE" value="true" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<enrich>
<source type="inline" clone="true">
<ax21:newvalue
xmlns:ax21="http://services.samples/xsd">testsamplevalue
</ax21:newvalue>
</source>
<target
xmlns:ax21="http://services.samples/xsd"
xmlns:ns="http://services.samples" action="sibling" xpath="//ns:getQuoteResponse/ns:return/ax21:volume"/>
</enrich>
<cache collector="true"/>
<respond/>
</inSequence>
</resource>
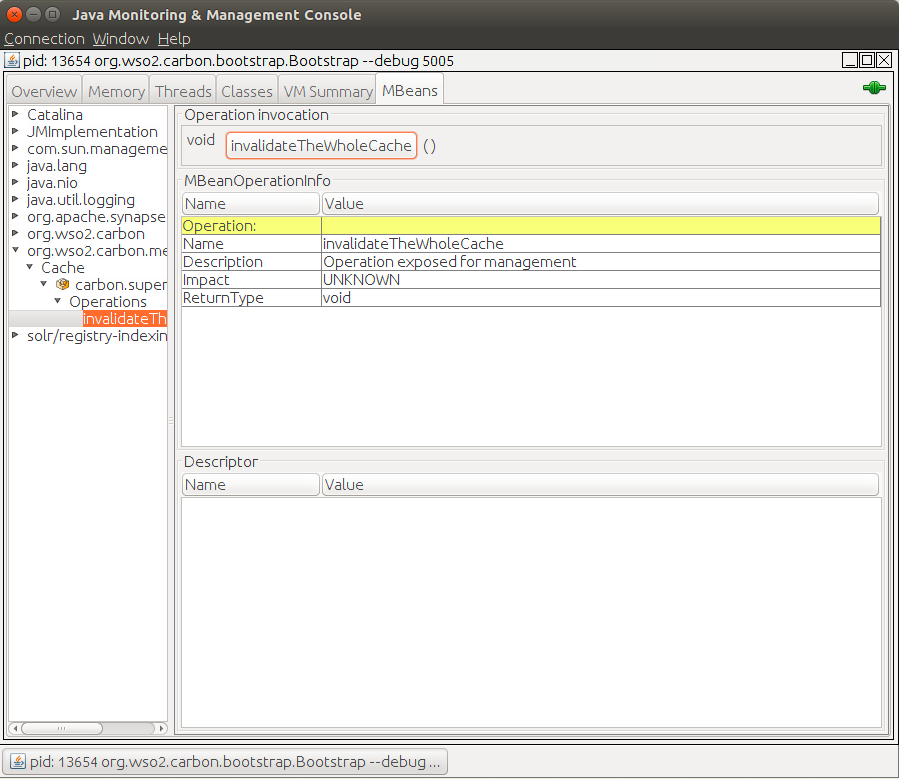
</api>Invalidating cached responses remotely¶
You can invalidate all cached response remotely by using any JMX monitoring tool such as Jconsole via the exposed MBeans. You can use the invalidateTheWholeCache() operation of the org.wso2.carbon.mediation MBean for this as shown below.