Sending a Simple Message to a Service¶
What you'll build¶
Let’s try a simple scenario where a patient makes an inquiry specifying the doctor's specialization (category) to retrieve a list of doctors that match the specialization. The required information is available in a back-end microservice.
To implement this use case, you will create a REST API resource and other artifacts using WSO2 Integration Studio, and then deploy them in the embedded WSO2 Micro Integrator instance. The default API resource will be configured to receive the client request in place of the back-end service, thereby decoupling the client and the back-end service. The response message with the requested doctor details will be routed back to the client through the same API resource.
Let's get started!¶
Step 1: Set up the workspace¶
- Download the relevant WSO2 Integration Studio based on your operating system. The path to the extracted/installed folder is referred to as
MI_TOOLING_HOMEthroughout this tutorial. -
Optionally, you can set up the CLI tool for artifact monitoring. This will later help you get details of the artifacts that you deploy in your Micro Integrator.
- Go to the WSO2 Micro Integrator website.
- Click Download -> Other Resources and click CLI Tooling to download the tool.
- Extract the downloaded ZIP file. This will be your
MI_CLI_HOMEdirectory. - Export the
MI_CLI_HOME/bindirectory path as an environment variable. This allows you to run the tool from any location on your computer using themicommand. Read more about the CLI tool.
Step 2: Develop the integration artifacts¶
Follow the instructions given in this section to create and configure the required artifacts.
Create the project directories¶
To create the required projects for this integration scenario:
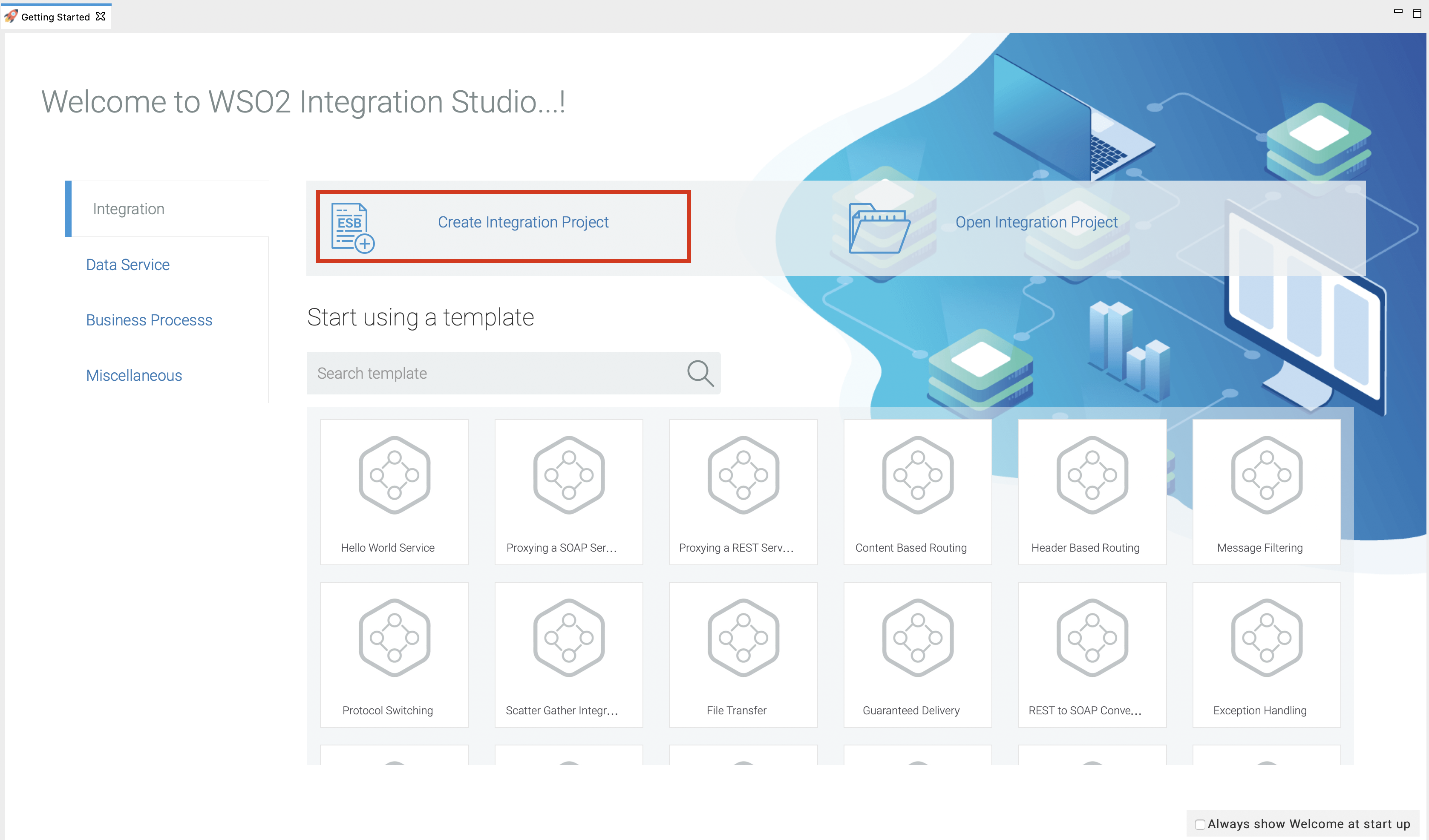
- Open WSO2 Integration Studio.
-
Go to Integration and click Create Integration Project.
-
Enter
SampleServicesas the project name and select the following check boxes.- Create Registry Resources Project
- Create Composite Application Project
- Create Connector Exported Project
Note
This will create a Config project named
SampleServicesalong with the Registry Resource project, Composite Application project, and a Connector Exporter project with the specified names.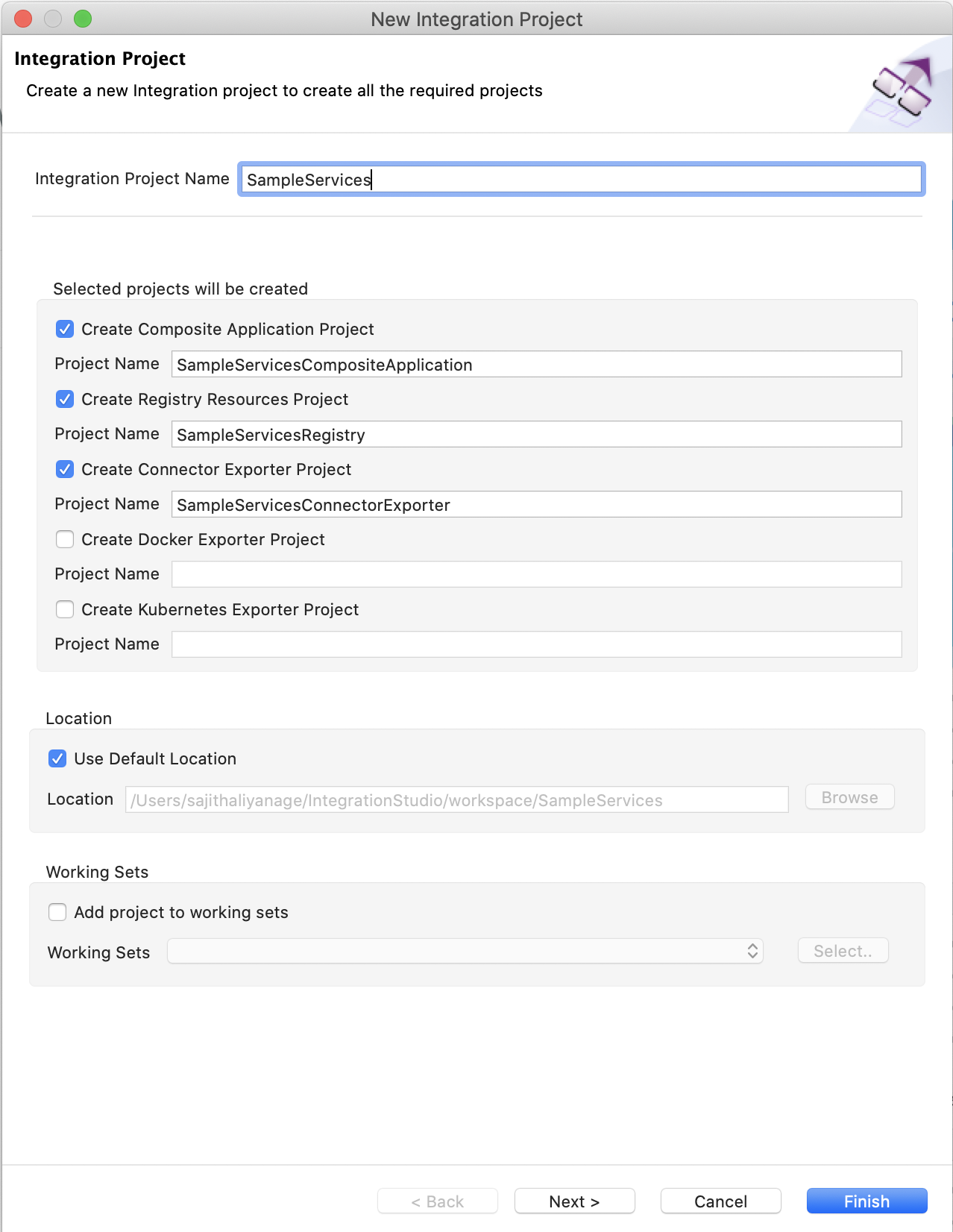
-
Click Finish.
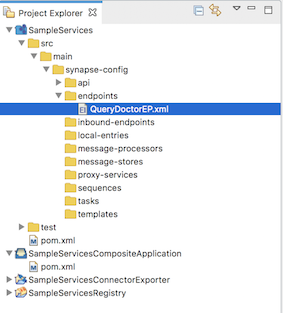
You can see the projects listed in the Project Explorer as shown below:
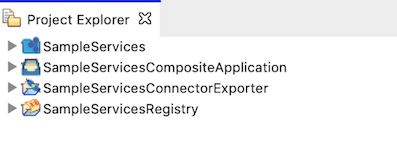
Create an Endpoint¶
An Endpoint artifact is required for the purpose of exposing the URL that connects to the back-end service.
- Right-click SampleServices in the Project Explorer and navigate to New -> Endpoint.
- Ensure that Create a New Endpoint is selected and click Next.
-
Enter the information given below to create the new endpoint.
Property Value Description Endpoint Name QueryDoctorEPThe name of the endpoint. Endpoint Type HTTP EndpointIndicates that the back-end service is HTTP. URI Template http://localhost:9090/healthcare/{uri.var.category}The template for the request URL expected by the back-end service. In this case, the variable 'category' that needs to be included in the request for querying doctors is represented as {uri.var.category}in the template.Method GETIndicates that we are creating this endpoint for GET requests that are sent to the back-end service. Static Endpoint
Select this option because we are going to use this endpoint only in this SampleServicesproject and will not reuse it in other projects. Note: If you need to create a reusable endpoint, save it as a Dynamic Endpoint in either the Configuration or Governance Registry.Save Endpoint in SampleServicesThis is the Config project where the artifact will be saved. 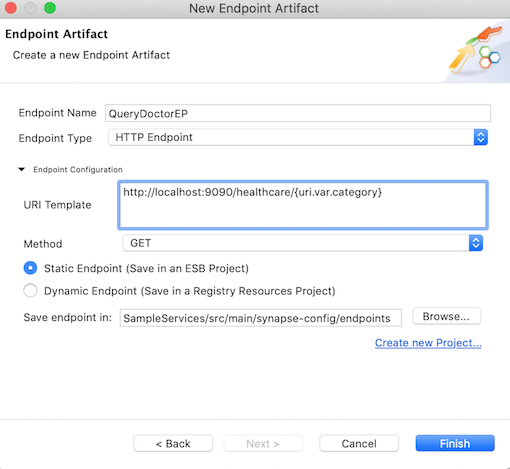
-
Click Finish.
The QueryDoctorEP endpoint is saved in theendpointsfolder within the Config project you created.
Create a REST API¶
A REST API is required for receving the client response and the REST resource within the API will define the mediation logic that will send requests to the Healthcare back-end service and retrieve the available doctor information.
- In the Project Explorer, right-click SampleServices and navigate to New -> REST API.
- Ensure Create A New API Artifact is selected and click Next.
-
Enter the details given below to create a new REST API.
|Property Value Description Name HealthcareAPIThe name of the REST API. Context /healthcareHere you are anchoring the API in the /healthcarecontext. This will become part of the name of the generated URL used by the client when sending requests to Healthcare service. For example, setting the context to /healthcare defines that the API will only handle HTTP requests where the URL path starts withhttp://host:port/healthcare.Save location SampleServices This is the Config project where the artifact will be saved. 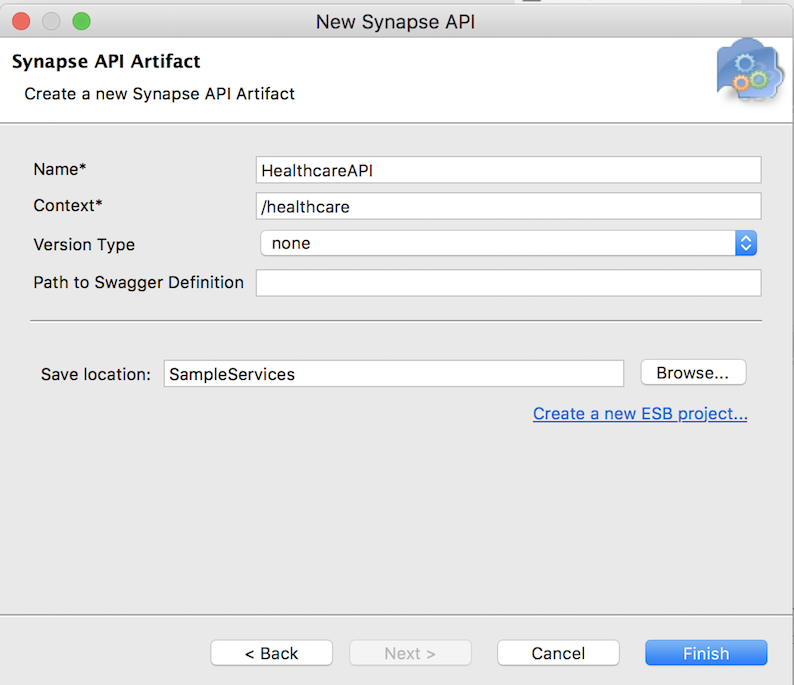
-
Click Finish.
Define the mediation flow¶
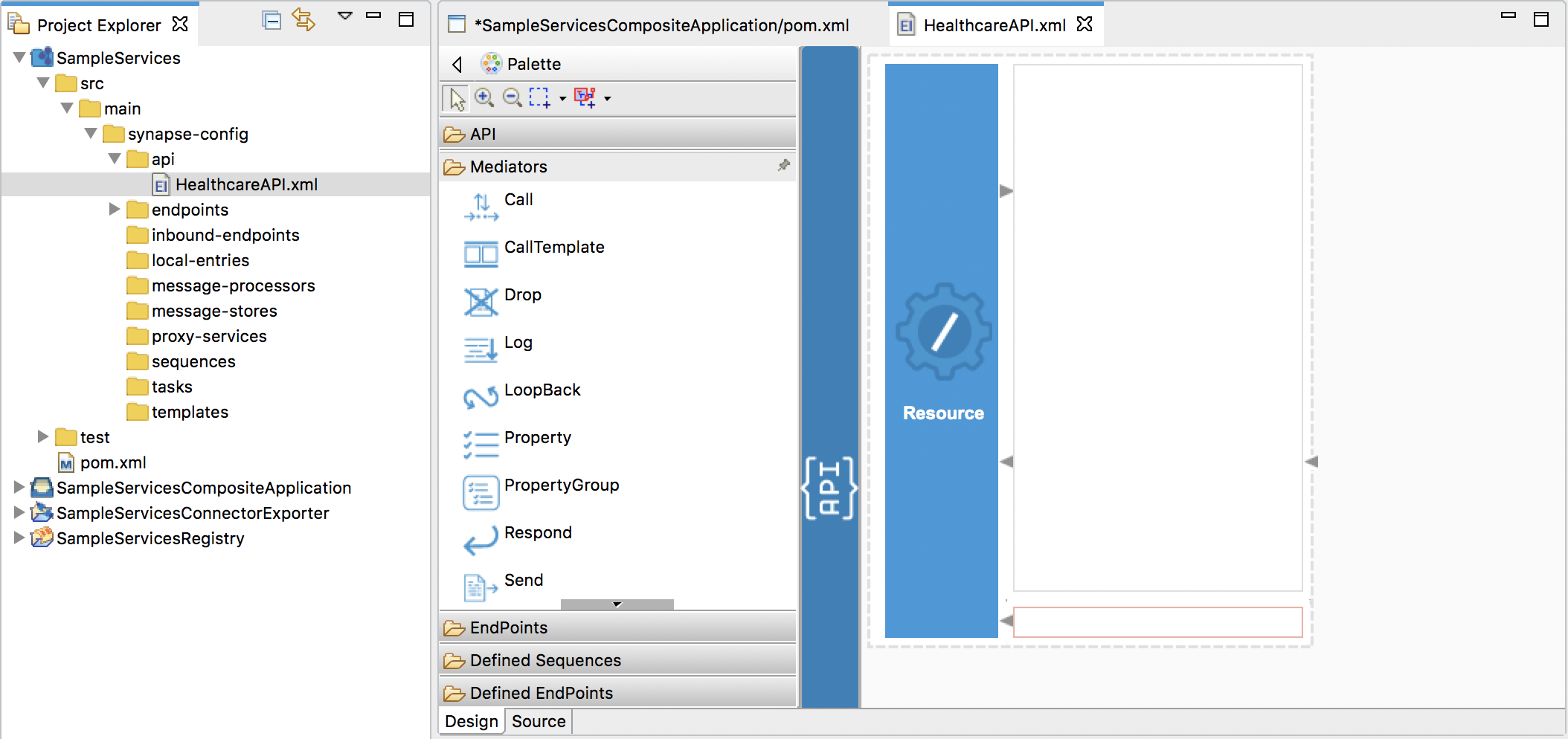
Once the API resource is created, the design view of the HealthcareAPI.xml file will appear as shown below.
Note
- The top part of the canvas is the In sequence, which controls how incoming messages are mediated.
- The middle part of the canvas is the Out sequence, which controls how responses are handled. In this case, a Send mediator is already in place to send responses back to the requesting client.
- The bottom part of the canvas is the Fault sequence, which allows you to configure how to handle messages when an error occurs (for more information, see Error Handling).
You can now start configuring the API resource.
- Double-click the Resource icon on the left side of the canvas.
The properties for the API resource appear on the Properties tab at the bottom of the window. If they do not appear, you can right-click the Resource icon and click Show Properties View. -
On the Properties tab, provide the following as Basic properties:
Property Description Url Style Click the respective Value field, click the down arrow, and then select URI_TEMPLATE from the list. URI-Template Enter /querydoctor/{category}. This defines the request URL format. In this case, the full request URL format ishttp://host:port/querydoctor/{category}where{category}is a variable.Methods Check if the value of Get is set to true. This defines that the API resource only handles the requests where the HTTP method is GET. 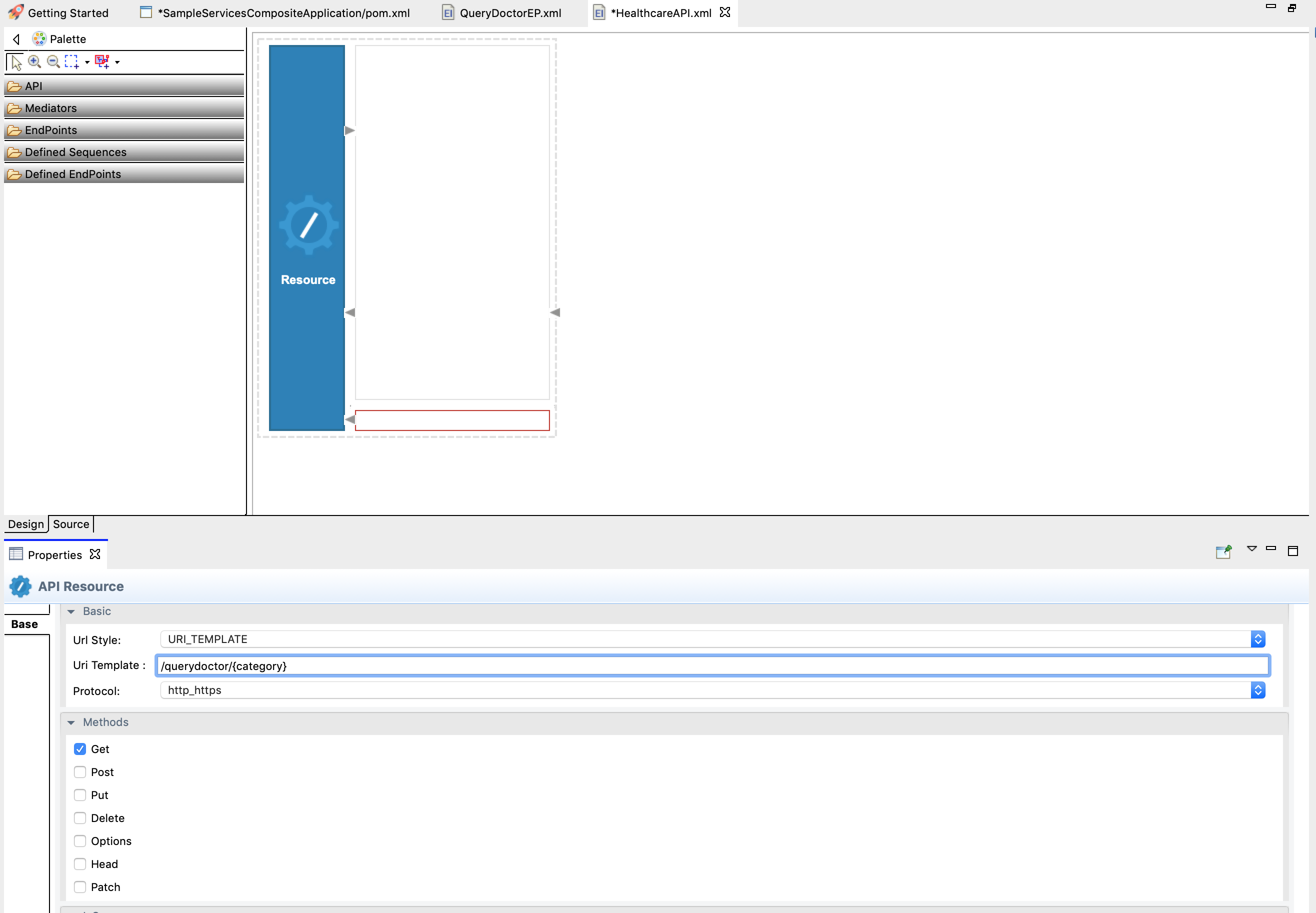
-
You can now configure the In sequence to handle requests from the client:
-
From the Mediators palette, click and drag a Log mediator to the In sequence (the top of the canvas).
Note
The Log mediator logs messages when the request is received by the In sequence of the API resource. In this scenario, let's configure the Log mediator to display the following message: “Welcome to the HealthcareService”.
-
With the Log mediator selected, access the Property tab and fill in the information in the table below:
Field Value Description Log Category INFOIndicates that the log contains an informational message. Log Level CustomWhen Customis selected, only specified properties will be logged by this mediator.Log Separator (blank)Since there is only one property that is being logged, you do not require a separator. Therefore, leave this field blank. Properties
To extract the stock symbol from the request and print a welcome message in the log, click the '+' icon in the Properties section, and then add the following values:
- Name:
Log Property message - Type:
LITERAL
(We select LITERAL because the required log message is a static value.) - Value/Expression :
"Welcome to HealthcareService"
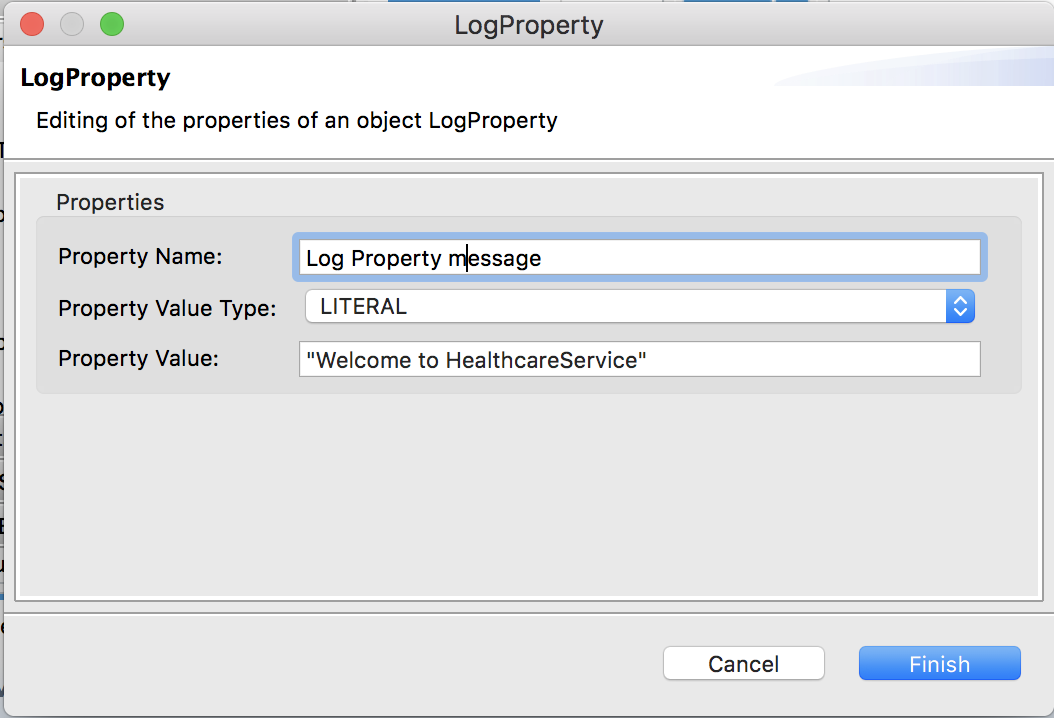
Description Request LogThe Description field provides the name that appears for the Log mediator icon in the design view. 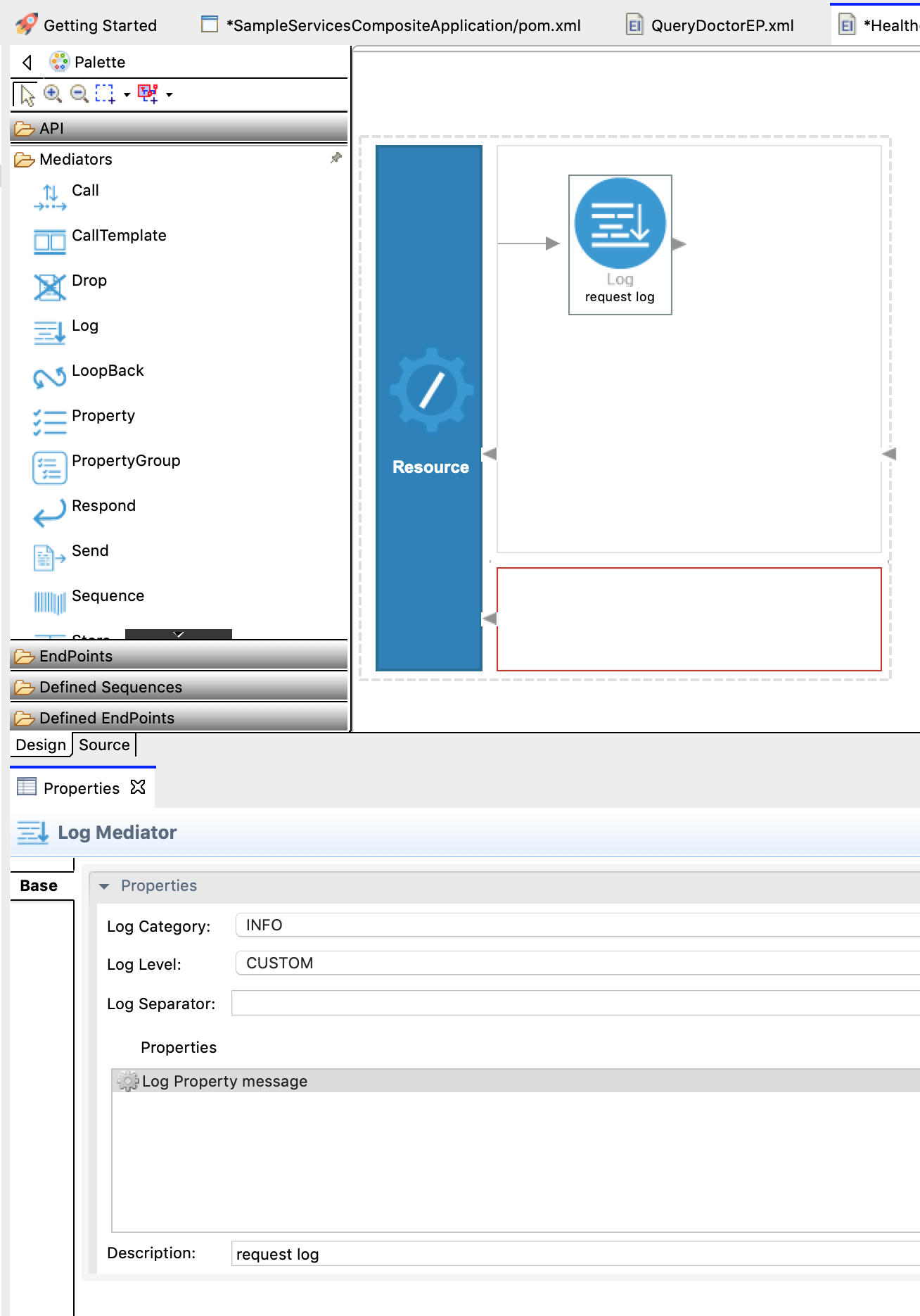
- Name:
-
Click OK to save the Log mediator configuration.
-
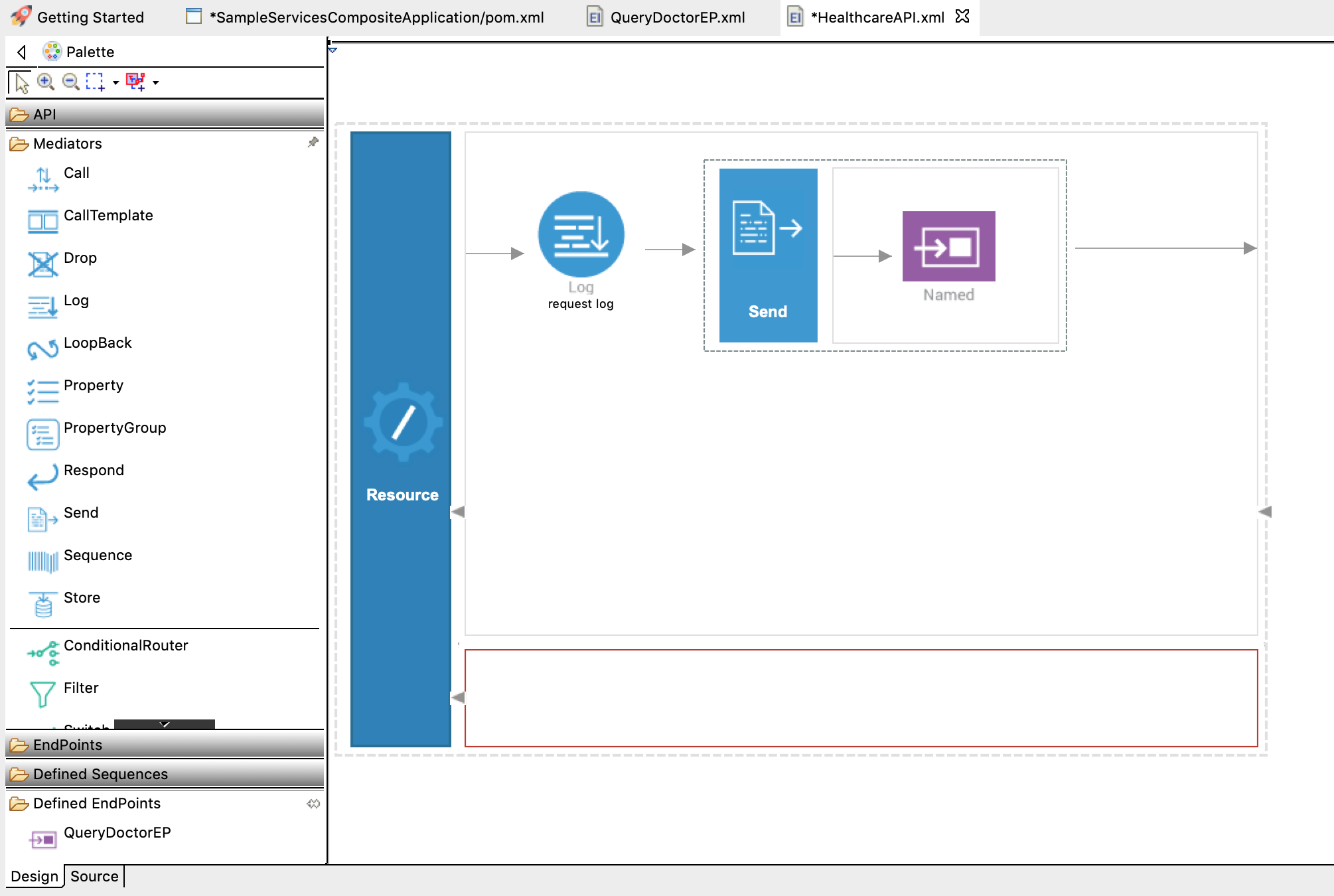
Configure the Send mediator to send the request message to the
HealthcareServiceendpoint.- From the Mediators palette, click and drag a Send mediator to the In sequence adjoining the Log mediator you added above.
- From the Defined EndPoints palette, click and drag the QueryDoctorEP endpoint, which we created, right next to the empty space of the Send mediator.
-
-
Configure the Out sequence to send the response from the Healthcare service back to the client.
For this, we use a Send mediator with no output endpoint defined, which defaults to sending the response back to the requesting client. From the Mediators palette, click and drag a Send mediator to the Out Sequence (the bottom part of the canvas).
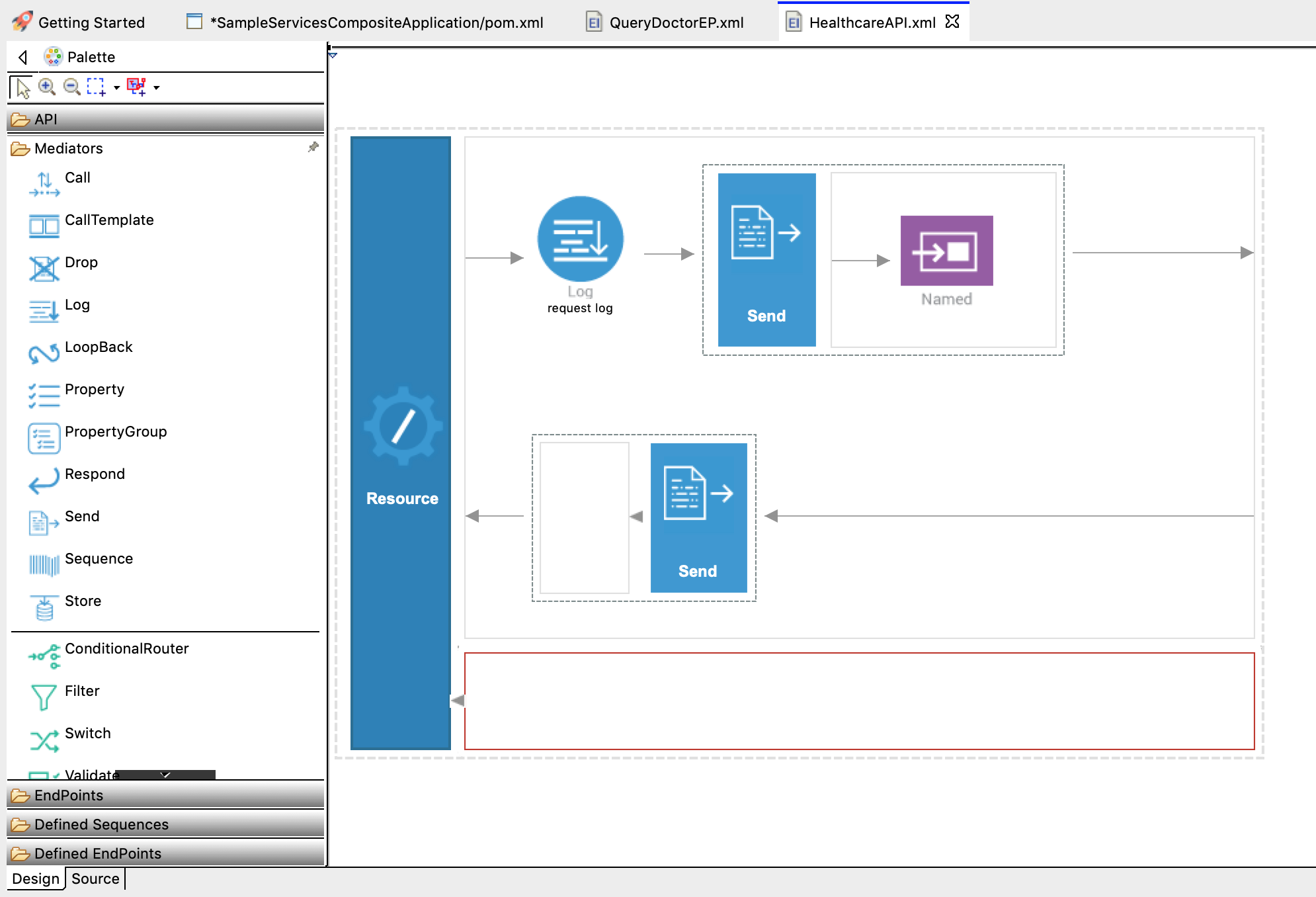
You have successfully created all the artifacts that are required for sending a request through the Micro Integrator to the back-end service.
Step 3: Package the artifacts¶
Package the artifacts in your composite application project (SampleServicesCompositeApplication project) to be able to deploy the artifacts in the server.
- Open the
pom.xmlfile in the composite application project POM editor. -
Ensure that the following artifacts are selected in the POM file.
HealthcareAPIQueryDoctorEP
-
Save the project.
Step 4: Build and run the artifacts¶
To test the artifacts, deploy the packaged artifacts in the embedded Micro Integrator:
- Right-click the composite application project and click Export Project Artifacts and Run.
- In the dialog that opens, select the artifacts that you want to deploy.
- Click Finish. The artifacts will be deployed in the embedded Micro Integrator and the server will start. See the startup log in the Console tab.
Step 5: Test the use case¶
Let's test the use case by sending a simple client request that invokes the service.
Start the back-end service¶
- Download the JAR file of the back-end service from here.
- Open a terminal, navigate to the location where your saved the back-end service.
-
Execute the following command to start the service:
java -jar Hospital-Service-2.0.0-EI7.jar
Get details of deployed artifacts (Optional)¶
Let's use the CLI Tool to find the URL of the REST API (that is deployed in the Micro integrator) to which you will send a request.
Tip
Be sure to set up the CLI tool for your work environment as explained in the first step of this tutorial.
-
Open a terminal and execute the following command to start the tool:
mi -
Log in to the CLI tool. Let's use the server administrator user name and password:
mi remote login admin adminYou will receive the following message: Login successful for remote: default!
-
Execute the following command to find the APIs deployed in the server:
mi api showYou will receive the following information:
NAME : HealthcareAPI
URL : http://localhost:8290/healthcare
Similarly, you can get details of other artifacts deployed in the server. Read more about using the CLI tool.
Send the client request¶
Let's send the request to the API. You can use the embedded HTTP Client of WSO2 Integration Studio as follows:
-
Open the HTTP Client of WSO2 Integration Studio.
Tip
If you don't see the HTTP Client pane, go to Window -> Show View - Other and select HTTP Client to enable the client pane.
-
Enter the request information as given below and click the Send icon (
 ).
).Method GETURL http://localhost:8290/healthcare/querydoctor/surgery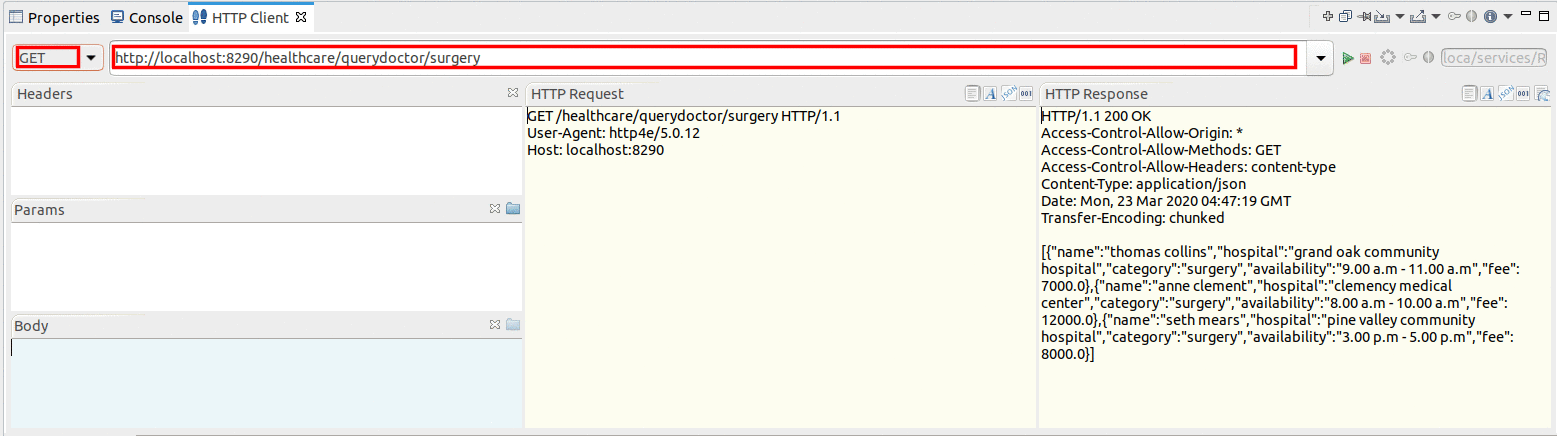
If you want to send the client request from your terminal:
- Install and set up cURL as your REST client.
- Execute the following command.
curl -v http://localhost:8290/healthcare/querydoctor/surgery
Analyze the response¶
You will see the response message from the HealthcareService with a list of available doctors and the relevant details.
[
{"name":"thomas collins",
"hospital":"grand oak community hospital",
"category":"surgery",
"availability":"9.00 a.m - 11.00 a.m",
"fee":7000.0},
{"name":"anne clement",
"hospital":"clemency medical center",
"category":"surgery",
"availability":"8.00 a.m - 10.00 a.m",
"fee":12000.0},
{"name":"seth mears",
"hospital":"pine valley community hospital",
"category":"surgery",
"availability":"3.00 p.m - 5.00 p.m",
"fee":8000.0}
]Now, check the Console tab of WSO2 Integration Studio and you will see the following message:
INFO - LogMediator message = "Welcome to HealthcareService"
You have now created and deployed an API resource in the Micro Integrator, which receives requests, logs a message using the Log mediator, sends the request to a back-end service using the Send mediator, and returns a response to the requesting client.
Top