K8s Deployment Sample 2: Content Based Routing¶
Let's define a content-based routing scenario using WSO2 Micro Integrator and deploy it on your Kubernetes environment.
Prerequisites¶
-
Install and set up WSO2 Integration Studio.
Tip
Be sure to get the latest updates before trying this example.
-
Install a Kubernetes cluster and v1.11+ client. Alternatively, you can run Kubernetes locally via Minikube.
- Install Docker.
- Install the EI Kubernetes operator.
Step 1: Create the integration solution¶
Follow the steps given below.
-
Create a Maven Multi Module project using WSO2 Integration Studio.
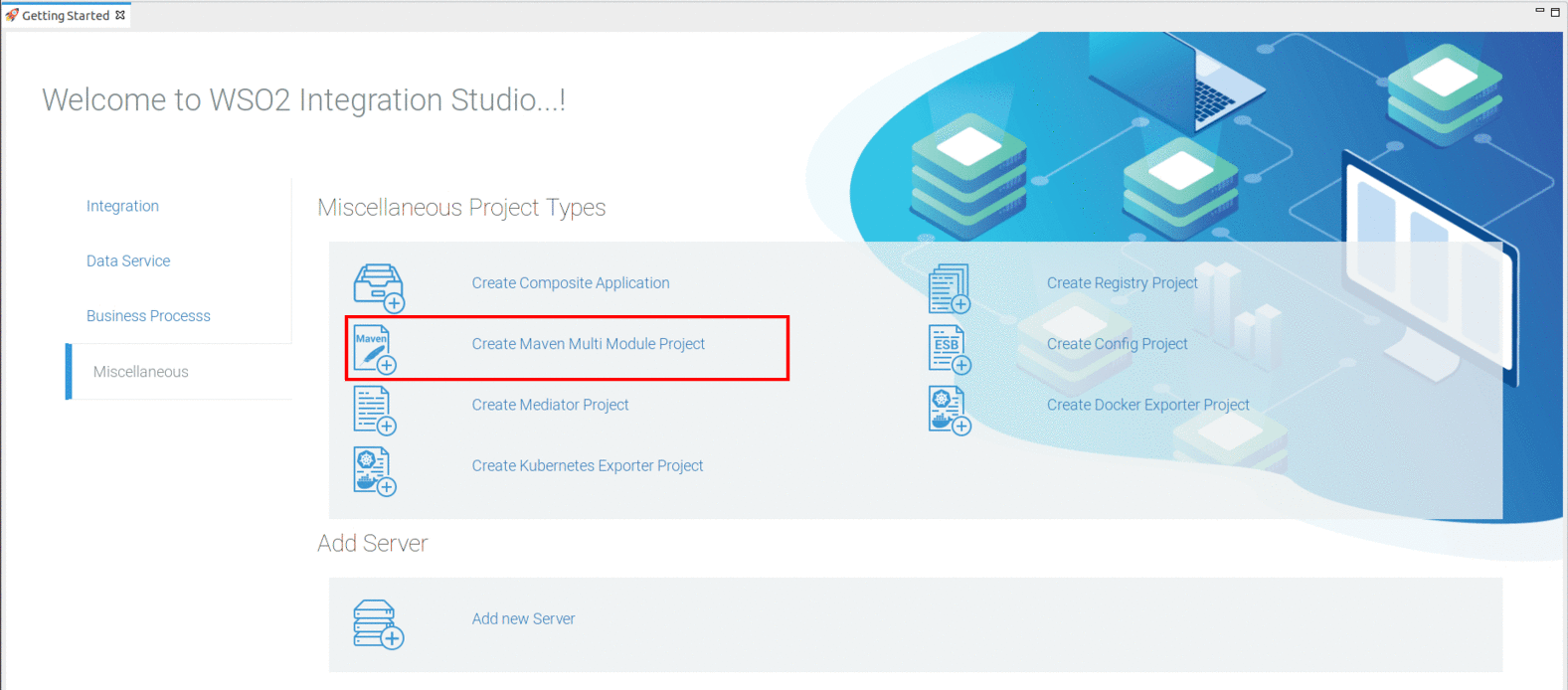
-
Create an ESB Config Project inside the Maven Multi Module project:
Right-click the Maven Multi Module project in the project explorer, go to New → Project, and select ESB Config Project to open the New ESB Config Project dialog.
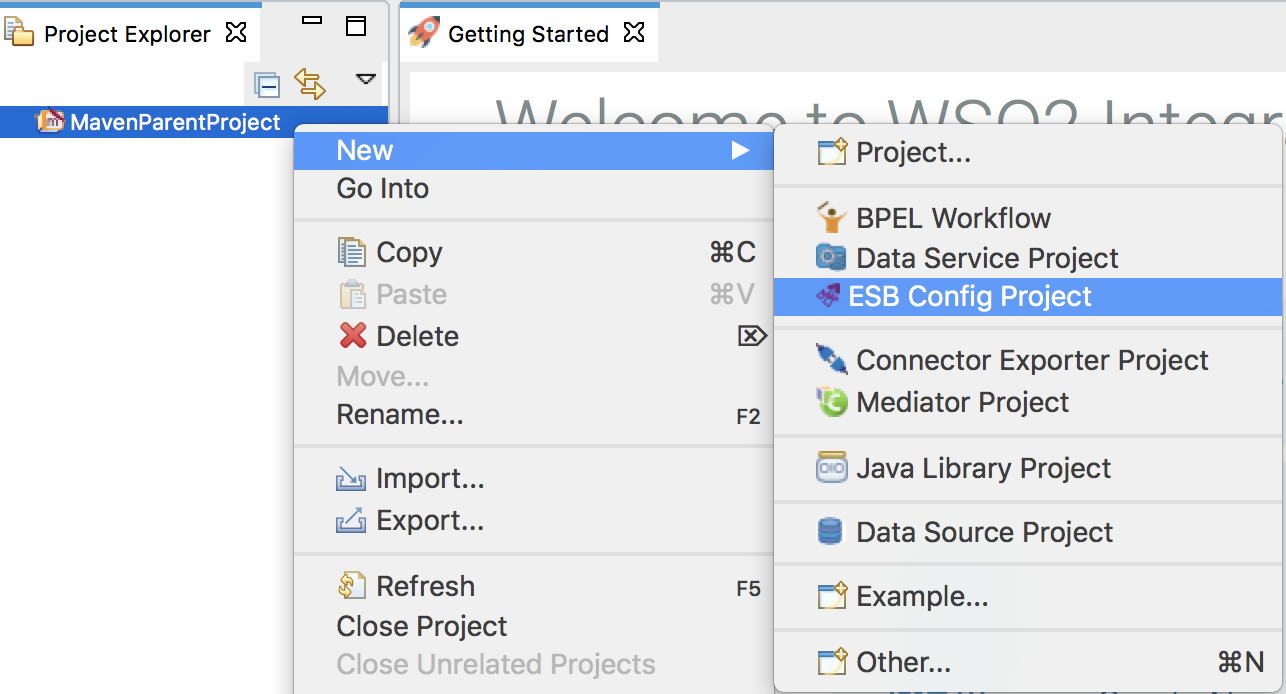
-
Add the following proxy service configuration inside the ESB Config Project. This service executes the arithmetic operation based on the input payload for each service request.
-
Right-click the ESB Config project in the project explorer, go to New -> Proxy Service and create a custom proxy service named
ArithmaticOperationService.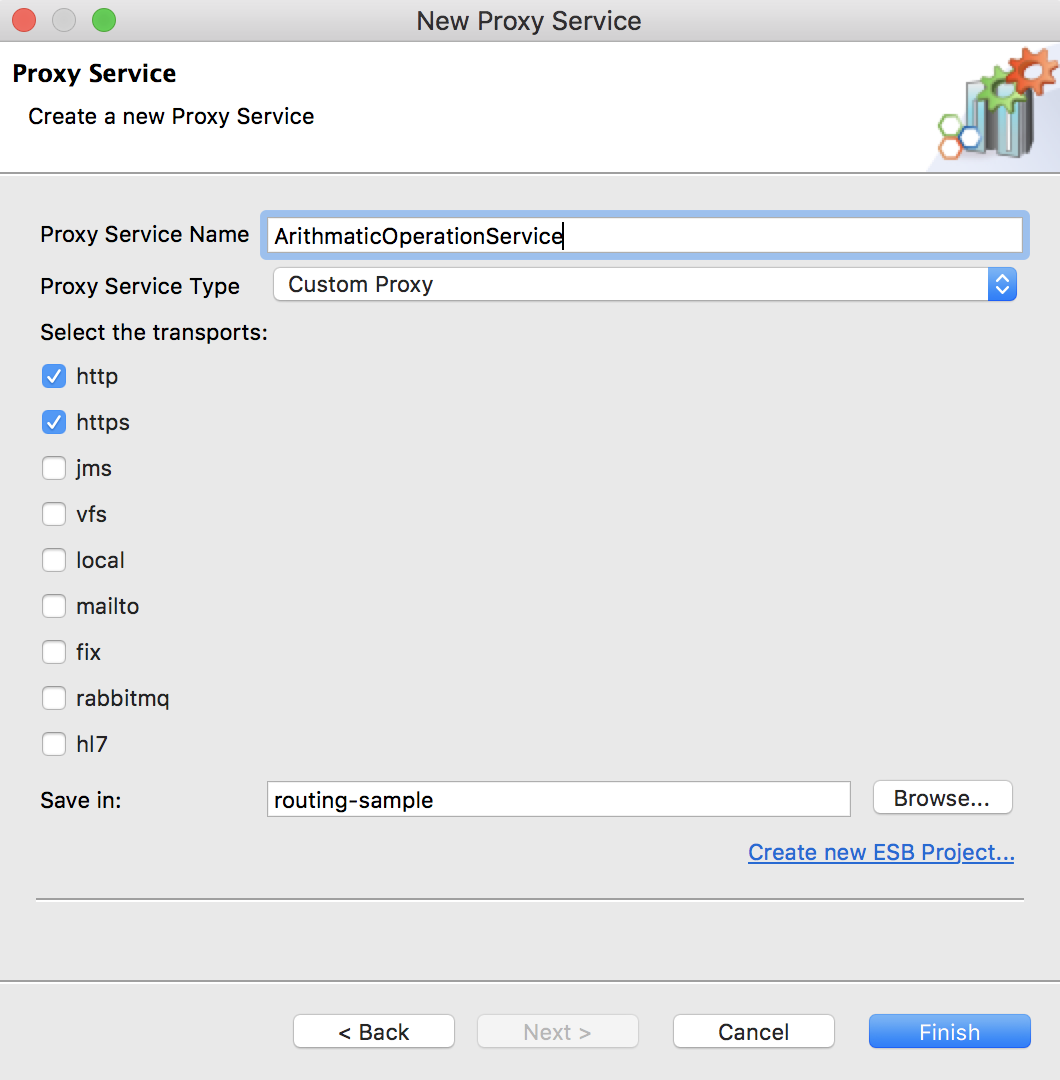
-
You can then use the Source View to copy the following configuration.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <proxy name="ArithmaticOperationService" startOnLoad="true" transports="http https" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <target> <inSequence> <log description="Log Request Payload" level="full"/> <switch description="Route based on the Operation" source="//ArithmaticOperation/Operation"> <case regex="Add"> <payloadFactory description="Construct payload for addition operation" media-type="xml"> <format> <tem:AddInteger xmlns:tem="http://tempuri.org"> <tem:Arg1>$1</tem:Arg1> <tem:Arg2>$2</tem:Arg2> </tem:AddInteger> </format> <args> <arg evaluator="xml" expression="//ArithmaticOperation/Arg1"/> <arg evaluator="xml" expression="//ArithmaticOperation/Arg2"/> </args> </payloadFactory> <header description="Set SOAPAction header" name="Action" scope="default" value="http://tempuri.org/SOAP.Demo.AddInteger"/> <call description="Send request to the endpoint"> <endpoint key="NumberAdditionEP"/> </call> </case> <case regex="Divide"> <payloadFactory description="Construct payload for division operation" media-type="xml"> <format> <tem:DivideInteger xmlns:tem="http://tempuri.org"> <tem:Arg1>$1</tem:Arg1> <tem:Arg2>$2</tem:Arg2> </tem:DivideInteger> </format> <args> <arg evaluator="xml" expression="//ArithmaticOperation/Arg1"/> <arg evaluator="xml" expression="//ArithmaticOperation/Arg2"/> </args> </payloadFactory> <header description="Set SOAPAction header" name="Action" scope="default" value="http://tempuri.org/SOAP.Demo.DivideInteger"/> <call> <endpoint key="NumberDivisionEP"/> </call> </case> <default> <payloadFactory description="Create response payload for unsupported operation" media-type="xml"> <format> <Message xmlns="">Unsupported operation.</Message> </format> <args/> </payloadFactory> </default> </switch> <respond description="Send result to the client"/> </inSequence> <outSequence/> <faultSequence/> </target> </proxy>
-
-
Add the following endpoint configurations inside the ESB Config project you created above.
-
Right-click the ESB Config project in the project explorer, go to New -> Endpoint and create a new endpoint with the following configurations:
Parameter Value Endpoint Name NumberAdditionEP Endpoint Type Address Endpoint Address http://www.crcind.com/csp/samples/SOAP.Demo.cls -
Repeat the above step and create another endpoint with the following configurations:
Parameter Value Endpoint Name NumberDivisionEP Endpoint Type Address Endpoint Address http://www.crcind.com/csp/samples/SOAP.Demo.cls -
After creating the endpoints, go to the Source View of the endpoint artifacts (in WSO2 Integration Studio) and add
format="soap11"to the endpoint address. The source view of the two endpoints will now look as follows:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <endpoint name="NumberAdditionEP" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <address format="soap11" uri="http://www.crcind.com/csp/samples/SOAP.Demo.cls"> <suspendOnFailure> <initialDuration>-1</initialDuration> <progressionFactor>1.0</progressionFactor> </suspendOnFailure> <markForSuspension> <retriesBeforeSuspension>0</retriesBeforeSuspension> </markForSuspension> </address> </endpoint><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <endpoint name="NumberDivisionEP" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <address format="soap11" uri="http://www.crcind.com/csp/samples/SOAP.Demo.cls"> <suspendOnFailure> <initialDuration>-1</initialDuration> <progressionFactor>1.0</progressionFactor> </suspendOnFailure> <markForSuspension> <retriesBeforeSuspension>0</retriesBeforeSuspension> </markForSuspension> </address> </endpoint>
-
-
Create a Composite Application Project with the above proxy service inside the Maven Multi Module project.
- Right-click the maven multi module project, go to New → Project, select Composite Application Project, and click Next.
-
Be sure to select all the integration artifacts under Dependencies as shown below.
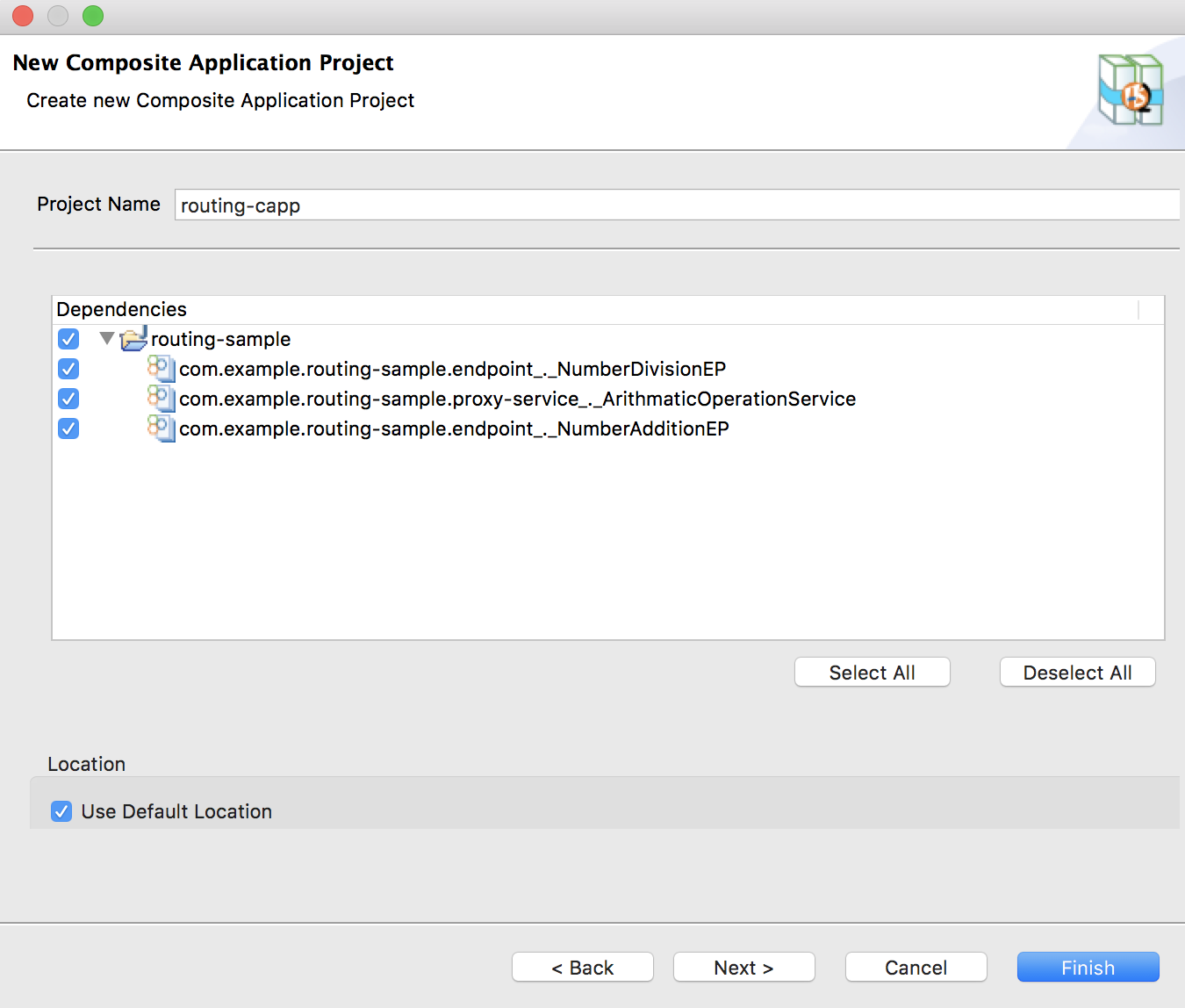
-
Click Finish.
-
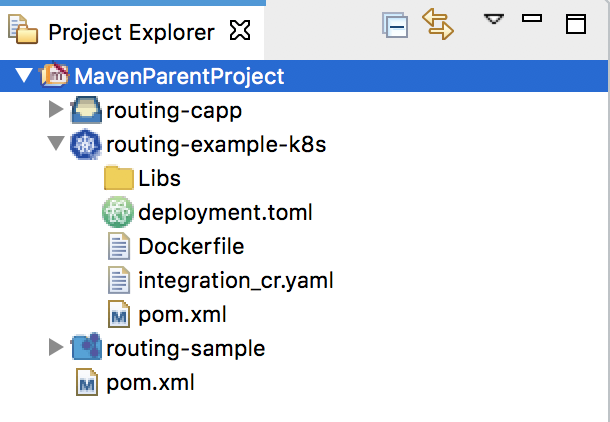
Create a Kubernetes Project inside the Maven Multi Module Project.
- Right-click the Maven Multi Module project, go to New → Project, select Kubernetes Exporter Project, and click Next.
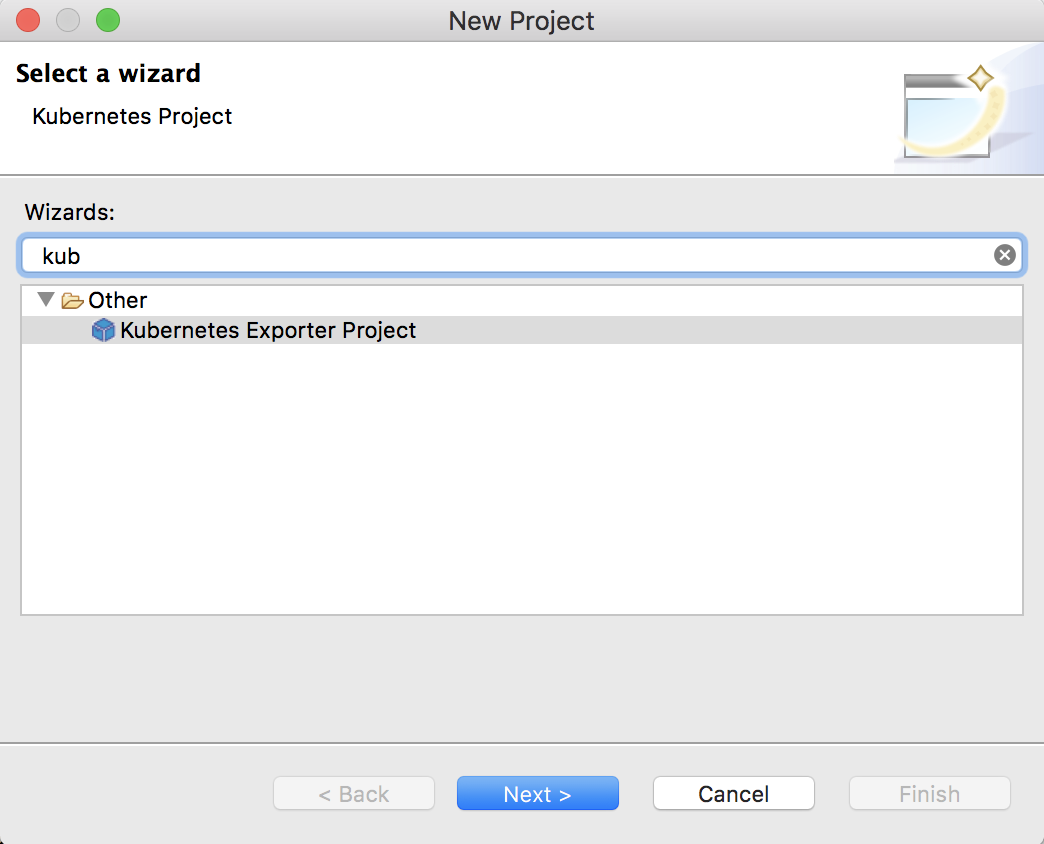
-
In the Kubernetes Project Information dialog that opens, enter the following details:
Parameter Description Kubernetes Project Name Give a unique name for the project. Integration Name This name will be used to identify the integration solution in the kubernetes custom resource. Let's use routing-exampleas the integration name for this example.Number of Replicas Specify the number of pods that should be created in the kubernetes cluster. Base Image Repository Specify the base Micro Integrator Docker image for your solution. For this example, let's use the Micro Integrator docker image from the WSO2 public docker registry: wso2/wso2mi. Note that the image value format should be 'docker_user_name/repository_name'. Base Image Tag Give a tag name for the base Docker image. Target Image Repository The Docker repository to which the Docker image will be pushed: 'docker_user_name/repository_name'. Target Image Tag Give a tag name for the Docker image. -
This step is only required if you already have a Docker image (in your local Docker repository) with the same name as the base image specified above.
Info
In this scenario, WSO2 Integration Studio will first check if there is a difference in the two images before pulling the image specified in the Base Image Repository field. If the given base image is more updated, the existing image will be overwritten by this new image. Therefore, if you are currently using an older version, or if you have custom changes in your existing image, they will be replaced.
To avoid your existing custom/older images from being replaced, add the following property under dockerfile-maven-plugin -> executions -> execution -> configurations in the
pom.xmlfile of your Kubernetes Exporter project. This configuration will ensure that the base image will not be pulled when a Docker image already exists with the same name.<pullNewerImage>false</pullNewerImage>Finally, the created Maven Multi Module project should look as follows:
- Right-click the Maven Multi Module project, go to New → Project, select Kubernetes Exporter Project, and click Next.
Step 2: Package and build the solution¶
You need to build a Docker image of the integration solution and push it to your Docker registry.
- Start the Docker daemon in the host machine.
-
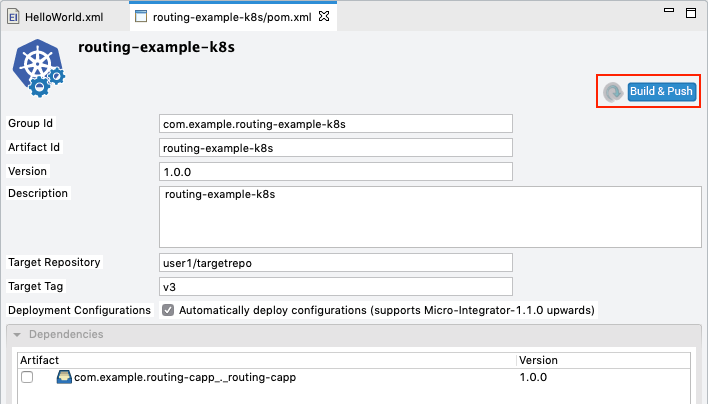
Open the POM file in the Kubernetes project, ensure that the composite application is selected under Dependencies, save the file.
-
Leave the Automatically deploy configurations check box selected. This ensures that deployment configurations are automatically deployed to the base image.
-
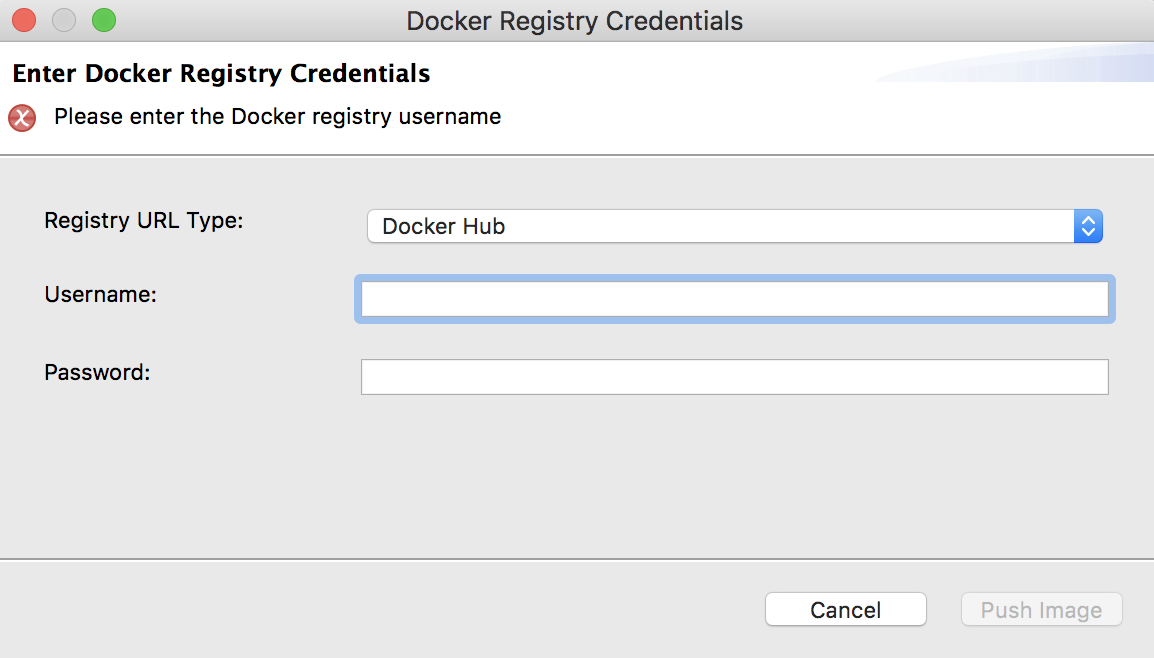
Click Build and Push. In the dialog that opens, enter the credentials of your Docker registry to which the image should be pushed.
Info
Alternatively, you can build the Docker image and push it to the Docker registry as follows:
- Navigate to the Maven Multi Module project and run the following command to build the project. It will create a docker image with the provided target repository and tag once the build is successfull.
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true - Navigate to the Kubernetes project inside the MavenParentProject and run the following command to push the docker image to the remote docker registry.
mvn dockerfile:push -Ddockerfile.username={username} -Ddockerfile.password={password}
- Navigate to the Maven Multi Module project and run the following command to build the project. It will create a docker image with the provided target repository and tag once the build is successfull.
-
Run the
docker image lscommand to verify that the Docker image is created.
Step 3: Deploy the solution in K8s¶
Info
Before you begin, be sure that the system requrements are in place, and that the EI Kubernetes Operator is installed.
Follow the steps given below:
- Ensure that your Kubernetes cluster is started.
- Open the
integration_cr.yamlfile from the Kubernetes project in WSO2 Integration Studio. -
See that the integration details of the
routing-examplesolution are updated:apiVersion: "integration.wso2.com/v1alpha2" kind: "Integration" metadata: name: "routing-example" spec: replicas: 1 image: "<Docker image for the Content-Based Routing Scenario>" -
Open a terminal, navigate to the location of your
integration_cr.yamlfile, and execute the following command to deploy the integration solution in the Kubernetes cluster:kubectl apply -f integration_cr.yaml
When the integration is successfully deployed, it should create the routing-example integration, routing-example-deployment, routing-example-service, and ei-operator-ingress as follows:
Tip
The ei-operator-ingress will not be created if you have disabled the ingress controller.
kubectl get integration
NAME STATUS SERVICE-NAME AGE
routing-example Running hello-service 2m
kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
routing-example-deployment 1/1 1 1 2m
kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
routing-example-service ClusterIP 10.101.107.154 <none> 8290/TCP 2m
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 2d
k8s-ei-operator ClusterIP 10.98.78.238 <none> 443/TCP 1d
kubectl get ingress
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ei-operator-ingress wso2ei 10.0.2.15 80, 443 2mStep 4: Test the deployment¶
Let's invoke the service without going through the ingress controller.
-
Create a
request.xmlfile as follows:
or<ArithmaticOperation> <Operation>Add</Operation> <Arg1>10</Arg1> <Arg2>25</Arg2> </ArithmaticOperation><ArithmaticOperation> <Operation>Divide</Operation> <Arg1>25</Arg1> <Arg2>5</Arg2> </ArithmaticOperation> -
Apply port forwarding as shown below. This will allow you to invoke the service without going through the Ingress controller:
kubectl port-forward service/routing-example-service 8290:8290 -
Execute the following command to invoke the service:
curl -X POST -d @request.xml http://localhost:8290/services/ArithmaticOperationService -H "Content-Type: text/xml"
You will receive the following SOAP response:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV='http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/' xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xmlns:s='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema'>
<SOAP-ENV:Body><AddIntegerResponse xmlns="http://tempuri.org"><AddIntegerResult>35</AddIntegerResult></AddIntegerResponse></SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>