Overview¶
Continuous integration and continuous delivery explained:¶
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Pipeline lays out some practices to follow to write code more quickly and ultimately generate value to the end-user. The CI (Continuous Integration) is the process of automatically detecting, pulling, building, and doing unit testing as source code is changed periodically for a product. CD(continuous Delivery) generally refers to the overall chain of processes (pipeline) that automatically gets source code changes and runs them through build, test, packaging, and related operations to produce a deplorable release, largely without any human intervention.
CI/CD Pipeline is crucial in order to improve delivery predictability, efficiency, security and maintainability of our products. This pipeline automates the steps in our product delivery process, such as initiating automatic builds, testing and then deploying to Kubernetes.
The Kubernetes Continuous Integration Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline tools for WSO2 Micro Integrator in help in automating the delivery process by building docker images, running automated tests, and deploying to a Development, Staging, or Production environment. Additionally, the setup consists of tools required for seamless update delivery, log aggregation, and monitoring.
The tools consist of Jenkins and Spinnaker. They are the primary tools used for continuous integration and deployment. The setup is deployed on top of Kubernetes using Helm, which makes the processes of configuration, installation, scaling, and upgrading simple. Additionally, Jenkins jobs and Spinnaker pipelines are preconfigured, making the process of getting started hassle-free.
Pipeline Architecture¶
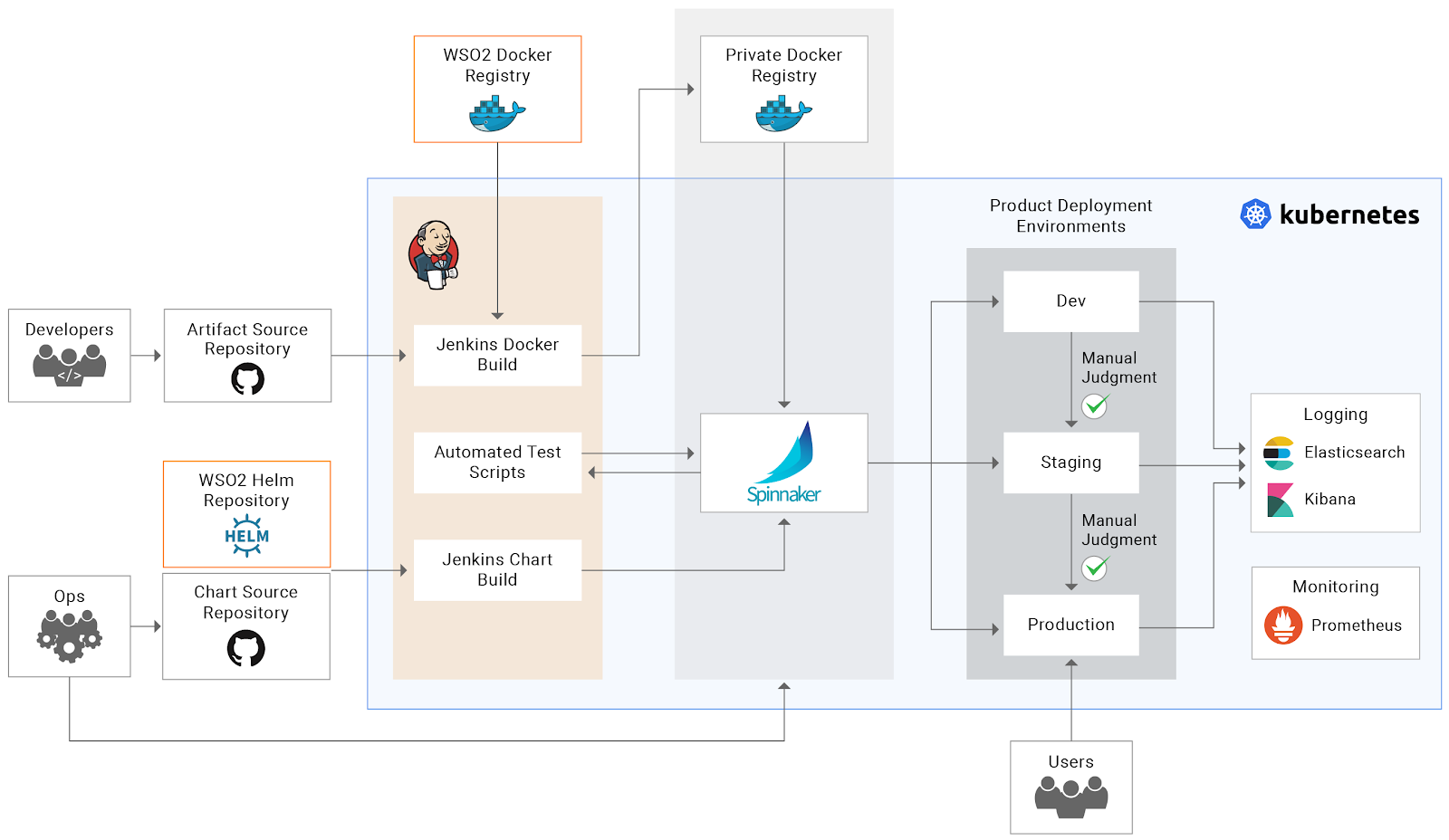
The following diagram illustrates the architecture of the CI/CD pipeline.
This pipeline uses Jenkins as the integration tool, while Spinnaker is being used as the deployment tool.
For a product to be created or updated, Spinnaker expects a new Helm chart or Docker image. An update could be triggered by Spinnaker from any of the following events:
-
The Helm chart's overridden values (
values-dev.yaml, values-staging.yaml, values-prod.yaml) are stored in the chart source repository and Jenkins periodically polls for changes to the repository. Once a change is detected, a predefined Jenkins job will download the relevant chart from WSO2 repository and provide it to Spinnaker as a Webhook along with the overrides for each environment. -
A cron job in Jenkins pulls the latest image from the WSO2 Docker registry containing the latest updates. A new image is built on top of this updated base image based on the Dockerfile in the artifact source repository. This image is then pushed to the private Docker registry which is then consumed by Spinnaker and propagated to the environments.
-
The artifact source repository contains a Dockerfile that is used to customize the base image from the WSO2 Docker registry. This could also include artifacts that need to be copied into the image. A change to this repository triggers a build of a new image, which gets pushed to the private Docker registry. This triggers Spinnaker to propagate the new image to the environments.
Each environment has a corresponding Spinnaker pipeline (Dev, Staging, and Production). Every new change is deployed to the Dev environment immediately. However, promotion to the staging and above environments need a manual approval, which will trigger the pipelines to respective environments.
Top